What Is a Chip Capacitor?
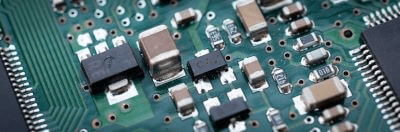
Chip capacitors are small capacitors made as chip components.
First of all, chip components are small surface-mount passive components in general. Chip components are made of capacitors, resistors, fuses, inductors, transformers, etc. All have fixed electrodes. Originally, flexible lead wires were used as electrodes in electronic components to be inserted into holes in printed circuit boards. Chip components are characterized by soldering small fixed electrodes to the board surface.
Due to limitations in heat resistance performance and size, chip capacitors can only be used in a limited number of dielectrics, and the following four types have been commercialized.
- Chip aluminum electrolytic capacitor
- Chip tantalum capacitors (including conductive polymer capacitors)
- Chip multilayer ceramic capacitor
- Chip mica capacitor
Uses of Chip Capacitors
Chip capacitors are very advantageous for the miniaturization of circuit boards because of their smaller component size and their compatibility with reflow soldering compared to leaded capacitors. Because of these features, chip capacitors were initially used in small products such as notebook PCs, cellular phones, and photographic equipment. They are now widely used in home appliances and electronic equipment because of their superior productivity, including the use of chip mounters.
Chip capacitors are no different from leaded capacitors in terms of characteristics. Chip capacitors exhibit desirable characteristics because the negative effects of the inductance component of the lead wires are eliminated.
When selecting a capacitor, the following characteristics should be taken into consideration.
1. Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are capacitors that use aluminum as the electrode. An oxide film is formed on the surface of the aluminum electrode by electrolysis, and this is used as the dielectric. Because of its low cost and high capacitance, it has been widely used as a high-capacitance capacitor. However, it also has the disadvantages of poor frequency characteristics and a tendency to suffer dielectric loss due to liquid leakage. In circuits where the capacitor is constantly energized, its short life at high temperatures can also be a problem.
2. Tantalum Capacitor
Tantalum capacitors use tantalum as the anode and tantalum pentoxide as the dielectric and are characterized by their small size and light weight despite their large capacitance. They are also superior to aluminum electrolytic capacitors in terms of leakage current characteristics, frequency characteristics, temperature characteristics, etc. On the other hand, the capacitor is relatively expensive because it is made of tantalum, a rare metal.
3. Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor
Depending on the type of ceramic used for the dielectric, capacitors are classified into two types: low-dielectric constant type and high-dielectric constant type. The low dielectric constant type has a low capacitance variation but does not have a large capacitance. The high dielectric constant type provides large capacitance, but its disadvantage is that the capacitance varies depending on the applied voltage and ambient temperature. Multilayer ceramic capacitors are small and heat-resistant, but they are prone to cracking and chipping and must be handled with care.
4. Mica Capacitor
Mica, a natural mineral, is used as the dielectric. It has a high- dielectric constant, is thin and peelable, and has excellent insulation resistance, dielectric loss tangent, frequency response, and temperature characteristics, but it is expensive and large.
Chip capacitors cannot be used in power equipment with high voltage and high current because of their small size. Large capacitors, such as oil capacitors, are conventionally used for motors, transformers, generators, etc.
Features of Chip Capacitors
The structural feature of chip capacitors is the fixed electrode, as described above. To ensure good solderability, the electrode is generally nickel-plated and then covered with tin plating. It is also advantageous in terms of miniaturization since there is no lead wire as an electrode.
On the other hand, because they are designed to be soldered in a reflow oven, chip capacitors are equipped with devices to improve heat resistance so that they can withstand an atmosphere of 240°C. Even so, care must be taken when soldering them. In particular, electrolytic capacitors that are sealed with electrolytic solution and tantalum capacitors that are solidified with resin on the exterior are exposed to high temperatures during soldering, which may cause deterioration and failure of the element due to thermal expansion of the electrolytic solution and resin. Film capacitors have extremely excellent capacitor characteristics, but the reason for the lack of chip components is that the film, which is the dielectric, cannot withstand the above thermal conditions.
Other Information on Chip Capacitors
Chip Capacitors Trends
The performance of chip capacitors is improving day by day. While improvements are being made in the characteristics of all types of capacitors, the demand for chip monolithic ceramic capacitors is growing rapidly. Chip monolithic ceramic capacitors are said to account for more than 80% of all capacitor production in terms of volume, with around 500 used in smartphones and 1,000 used in notebook PCs. They have become an indispensable component not only in electronic devices but also in automobiles, which are becoming increasingly computerized. The main reasons for this are miniaturization and high capacitance. The size of chip monolithic ceramic capacitors has been getting smaller year by year, with the 0603 type (0.6 x 03 mm) now the mainstream, but the 0201 type (0.2 x 0.1 mm) has already started to be put into practical use. As miniaturization progresses and mounting density increases, the substrate area becomes smaller, contributing to product miniaturization.
Meanwhile, even in applications where large capacitors such as aluminum electrolytic and tantalum capacitors are the mainstream, chip multilayer ceramic capacitors are gradually replacing them. This is due to improvements in the dielectric constant of materials, thinner dielectric layers, multiple layers, and higher reliability. The major advantage of multilayer ceramic capacitors is they are easy to use and free from the fear of leakage in aluminum electrolytic capacitors and ignition in tantalum capacitors.
Under these circumstances, it is expected that multilayer ceramic capacitors will continue to play a leading role in chip capacitors and be used in various fields in the future.