What Is a Choke Coil?
 A choke coil is an element used in electrical circuits and is a type of inductor optimized for use as a choke.
A choke coil is an element used in electrical circuits and is a type of inductor optimized for use as a choke.
The meaning of choke in this case refers to the ability to keep AC currents above a certain frequency relatively high and to facilitate the passage of currents below that frequency, and is implemented in an electrical circuit.
The typical coil construction consists of a laminated plate of silicon copper or other steel plate as the core (iron core), around which conductors are wound in a spiral shape.
There are three types of choke coils: smoothing choke coils, active filter choke coils, noise filter choke coils, and power line choke coils. Each is used for different purposes.
Uses of Choke Coils
As mentioned above, there are four major types of choke coils depending on the application.
1. Smoothing Choke Coils
Choke coils are used to reduce the distortion of the current when AC current is converted to DC by a smoothing circuit or AC/DC converter, and to smooth the current.
2. Choke Coil for Active Filter
Used as a high-frequency countermeasure in active filters used in analog signal input circuits such as measuring instruments.
3. Choke Coil for Noise Filter
Choke coils are mounted in power supply circuits that are prone to noise inflow and used as noise countermeasures.
4. Choke Coil for Power Supply Line
Choke coils are used to match the load of RF power amplifiers and to reduce impedance resistance and losses in power supply lines.
Principle of Choke Coil
A choke coil consists of a core made of a laminated plate of silicon copper or other steel plate, around which conductors are wound in a spiral shape.
The choke coil is characterized by a higher inductance value than the coils used in general.
General coils and choke coils differ in the following characteristics:
- General coil
Easy to conduct direct current and difficult to conduct alternating current. - Choke Coil
Easy to carry DC current and low frequency AC current, and hard to carry high frequency AC current.
The reason why choke coils have the above characteristics is that they have a high inductance value and when an AC current of high frequency flows, an induced electromotive force is generated, which is opposite to the direction of the current flow, making it difficult for the current to flow.
When used as an active filter or for noise suppression, external noise that attempts to flow into a measurement device from its input terminal or power supply terminal of a power circuit has a high frequency. Choke Coils are often used in such applications because they can block high-frequency noise.
Other Information on Choke Coils
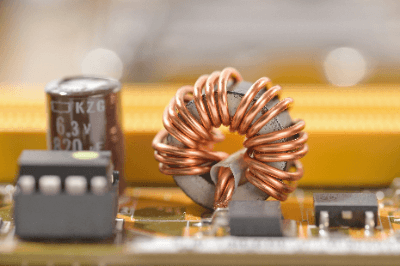
1. About Toroidal Coils
Choke Coils are often made by winding a conductor around a doughnut-shaped magnetic core, unless they are ultra-compact chip components, such as those used in smartphones. This is called a toroidal coil and can confine the magnetic flux in a closed loop (right-hand thread law). The advantage of toroidal coils is that they can achieve a larger inductance in a smaller size by utilizing this confined magnetic flux.
Important factors for inductor characteristics include Q-value and maximum allowable current. Based on the recent demand for compact, high-density packaging, manufacturers are competing to improve these inductor characteristics while reducing the size of the inductors.
2. Material of Magnetic Core
Various materials are used for the magnetic core of a choke coil, including laminated steel plates. One of the most commonly used magnetic core materials is ferrite material, which can be broadly classified into nickel-based and manganese based materials.
Nickel-based ferrite materials have very high insulation properties and are often used at high frequencies above 100 MHz.
Manganese-based ferrite materials are inexpensive and have high magnetic permeability and saturation flux density, and are often used in common mode chokes for low-frequency power lines.