What Is a Non-Contact Temperature Sensor?
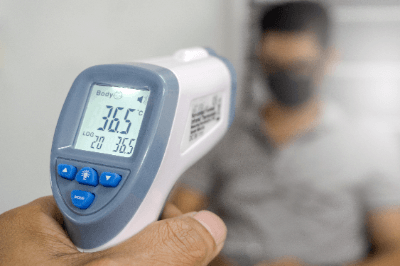 A non-contact temperature sensor is a sensor that can detect temperature without being directly attached to the object being measured.
A non-contact temperature sensor is a sensor that can detect temperature without being directly attached to the object being measured.
They use infrared rays emitted by an object or scattered by incident neutrons. Most non-contact temperature sensors on the market are infrared sensors. Infrared rays are detected using a sensing element, and the emissivity is used to calculate the temperature of the object being measured. Emissivity is the amount of infrared radiation relative to the surface temperature determined for each object, and is necessary when using non-contact temperature sensors.
Non-contact sensors have a specific range or distance over which they can measure, and the range over which they can measure is called the spot diameter. The smaller the spot diameter is compared to the object or person being measured, the more stable the temperature can be measured. In addition, when measuring high-temperature objects, it is necessary to take measures such as cooling the non-contact temperature sensor to prevent it from being damaged due to the heat generated by the sensor itself.
Uses of Non-Contact Temperature Sensors
Non-contact temperature sensors are used in a wide range of applications, from everyday life to industrial use. The following are examples of non-contact temperature sensor applications.
- Measuring the temperature of food during the baking process in food factories
- Temperature measurement to determine the degree of drying of industrial products after painting
- Measurement of product temperature distribution during lathing
- Measurement of body temperature
Non-contact temperature sensors are used in situations where it is difficult or impossible to measure with contact-type temperature sensors. Specifically, they are used for moving or rotating objects.
It is also used to measure body temperature. They are used in numerous situations, such as in restaurants and when going to work in an office. Compared to contact thermometers that are inserted under the arm, the advantages of these thermometers are that they measure temperature faster and are more hygienic, eliminating the need to disinfect them after each use.
On the other hand, because they use infrared rays, they are greatly affected by external factors such as ambient temperature and sunlight. In addition, they are less accurate than contact sensors. It is necessary to adjust the temperature calculation method and improve the environment while taking into consideration the location where the non-contact temperature sensor will actually be utilized.
Principle of Non-Contact Temperature Sensors
A non-contact temperature sensor using infrared rays consists of a light-collecting lens, thermopile, amplifying amplifier, and arithmetic unit. Temperature is measured in the following sequence
1. Infrared Light Collection
Infrared light is invisible from 0.7 to 1,000 μm. Within this frequency range, only frequencies between 0.7 μm and 20 μm are used for practical temperature measurements.
This light is focused using an infrared condenser lens. By focusing infrared rays in the wavelength range detectable by the thermopile, measurement accuracy can be improved.
2. Conversion to Electrical Signals
Thermopiles are used to convert infrared rays into electrical signals for output. The thermopile is an infrared detection element that outputs an electrical signal in response to the temperature heated by infrared rays.
Within the thermopile, multiple thermocouples are connected in series with the warm junction facing the center, and an infrared absorbing film is placed at the center where the warm junction faces. Light collected by the lens hits only the warm junction, creating a temperature difference between the warm junction and the cold junction on the outside. This creates a voltage difference due to the Seebeck effect, enabling temperature measurement.
3. Amplification of Electrical Signals
An amplifying amplifier is used to amplify the electrical signal emitted from the thermopile. Amplification enables detection with higher accuracy.
4. Calculating Temperature From Emissivity
Corrections are made to calculate the temperature of the object to be measured. Emissivity is used for the correction. Emissivity is the ratio of the amount of infrared radiation emitted to the surface temperature of an object, which is a constant value for each object.
The temperature of the object to be measured is calculated using the amount of infrared radiation detected from the electrical signal converted by the thermopile and the emissivity of the object to be measured, which is measured in advance.
Types of Non-Contact Temperature Sensors
Non-contact temperature sensors can be classified into portable and installed types.
1. Portable Type
Portable sensors are held by a person and used to measure temperatures. Since it does not require a power supply, it can be easily carried around. They are lightweight, compact, and often inexpensive, ranging from several thousand yen to several tens of thousands of yen.
2. Installation Type
The target object passes in front of the device, and the temperature can be measured automatically without human intervention. Many of these products combine a thermographic camera and other equipment, and are often expensive, ranging from several hundred thousand yen to several million yen. The measurement does not require the user to touch the device, and depending on the device, measurements can be taken from a distance of 0.5 to 1.5 meters.