What Is a Noise Filter?
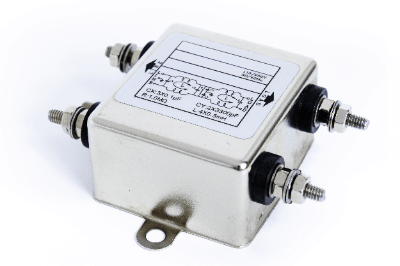 A noise filter is an electronic component used to remove noise from a power supply or signal.
A noise filter is an electronic component used to remove noise from a power supply or signal.
It is used in many electric and electronic circuits. When the current value in a communicating cable changes, a magnetic field is generated in the surrounding area. This magnetic field generates noise (abnormal signals) in the surrounding cable.
Noise filters can be installed to prevent the generation of noise. Note that using a device without noise filtering may cause malfunctions or failures.
Uses of Noise Filters
Noise filters are widely used in acoustic and industrial equipment.
The following are examples of noise filter applications:
- Prevention of noise in speakers
- Prevention of noise inside radio equipment
- Power supply lines of PLCs, PCs, and servers
- Inverter power circuits and thyristor power circuits
Noise filters are mainly used for receiving equipment that want to avoid noise and for output equipment that generates noise. Speakers and radios are devices that you want to eliminate the effects of noise, and noise filters are attached to communication lines. In this case, noise is a source of noise.
Computers such as PLCs also want to avoid malfunctions caused by noise, so noise filters are sometimes attached to power supply lines and so on. On the other hand, inverters and thyristors are devices that generate noise.
Since current and voltage changes in the secondary side circuit may be steep, noise filters are used to remove generated noise by smoothing it out. When smoothing the generated current, a reactor is generally used.
Principle of Noise Filters
Noise is transmitted in two main ways: radiation noise, which is radiated directly into space from inside electronic equipment, and conducted noise, which is transmitted through power supply lines and electronic circuit wiring and causes interference to other electronic equipment. It is generated as noise, for example, when radio waves of different wavelengths are introduced into radio waves of various wavelengths.
To prevent this noise, a filter (low-pass filter) is used to cut high-frequency signals if the main cause of the noise is high frequency. On the other hand, if the noise is low-frequency, a filter that cuts low-frequency signals (high-pass filter) is used.
Inductors and capacitors are the most common types of filters that act as low-pass filters. An inductor has a low impedance for low-frequency signals and a high impedance for high-frequency signals. Therefore, inserting an inductor in series in a circuit, allows low-frequency signal components to pass through more easily, while allowing high-frequency components to pass through less easily.
Capacitors, on the other hand, have the opposite characteristics of inductors. Combining a capacitor and an inductor makes a noise filter that cuts low and high frequencies.
How to Select a Noise Filter
Two important factors in selecting a noise filter are the rated voltage and the rated current.
1. Rated Voltage
Use a voltage lower than the rated voltage (maximum operating voltage) specified for each product. Some manufacturers take voltage fluctuations into account and may allow the use of a voltage higher than the rated voltage.
2. Rated Current
As with voltage, each product has its own upper limit for current. In particular, current characteristics tend to change depending on the ambient temperature, so it is necessary to check the environment in which the product will be used in advance.
As the ambient temperature rises, the allowable load current gradually decreases. Although a current in excess of the allowable current will not cause a serious problem for a short period of time, repeated current flow may cause a failure. In addition, DC power supplies, etc., may generate inrush currents, and noise filters should be selected by considering the current value and duration of the inrush current.
Other Information on Noise Filters
Precautions for Using Noise Filters
Ground wiring is also important for noise filters. The ground wiring should be as thick and short as possible. If the ground wire is long, an inductance component will act on it, which may degrade the attenuation characteristics.
It is also important not to tie input/output wires together or wire them close together. If the input/output wiring is close together, high-frequency noise components will bypass the filter and the desired filtering effect will not be achieved.