What Is a Water Meter?
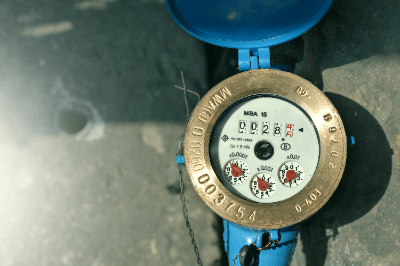
A water meter is an instrument used to measure and record water consumption, typically in municipal water supply systems. It is essential for calculating tap water usage fees and is regulated under the Measurement Act. Water meters must be produced by manufacturers authorized as specific measuring instrument production sites, and they have set expiration dates after which they cannot be used for fee determination.
Authorized production sites can be verified on the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s website.
Uses of Water Meters
Water meters are commonly used in residential and commercial settings. In residences, they are installed in easily accessible areas like entrances or basements. Meter readings, conducted monthly or more frequently by local authorities, are used to calculate water bills. For corporations, water meters are installed on both supply and intake lines for accurate billing and usage tracking.
Non-certified water meters can be used for non-billing purposes, such as in factory line management and other applications where no charges are involved.
Principle of Water Meters
Water meters are a type of flow meter.
The impeller-type flow meter is widely used for measuring water flow. In this meter, water flow rotates an impeller, with the rotation rate indicating the flow rate. This direct measurement method requires no external power and is highly accurate for tap water, which typically contains minimal impurities.
Electromagnetic flow meters are another option, particularly suitable for tap water due to its conductivity. They work by applying an electromagnetic force perpendicular to the flow and measuring the resulting electromotive force. While they require external power, many models include batteries that last for the meter’s specified lifespan.