What Is a Robot Cable?
Robot cables are used to transmit power and signals to robot arms and industrial robots.
Compared to general-purpose cables, they are characterized by extremely high durability against repeated bending and twisting. A variety of product cables are available on the market, including those that can handle high currents, those with small diameters, and those that bundle power and signal cables into a single cable.
Uses of Robot Cables
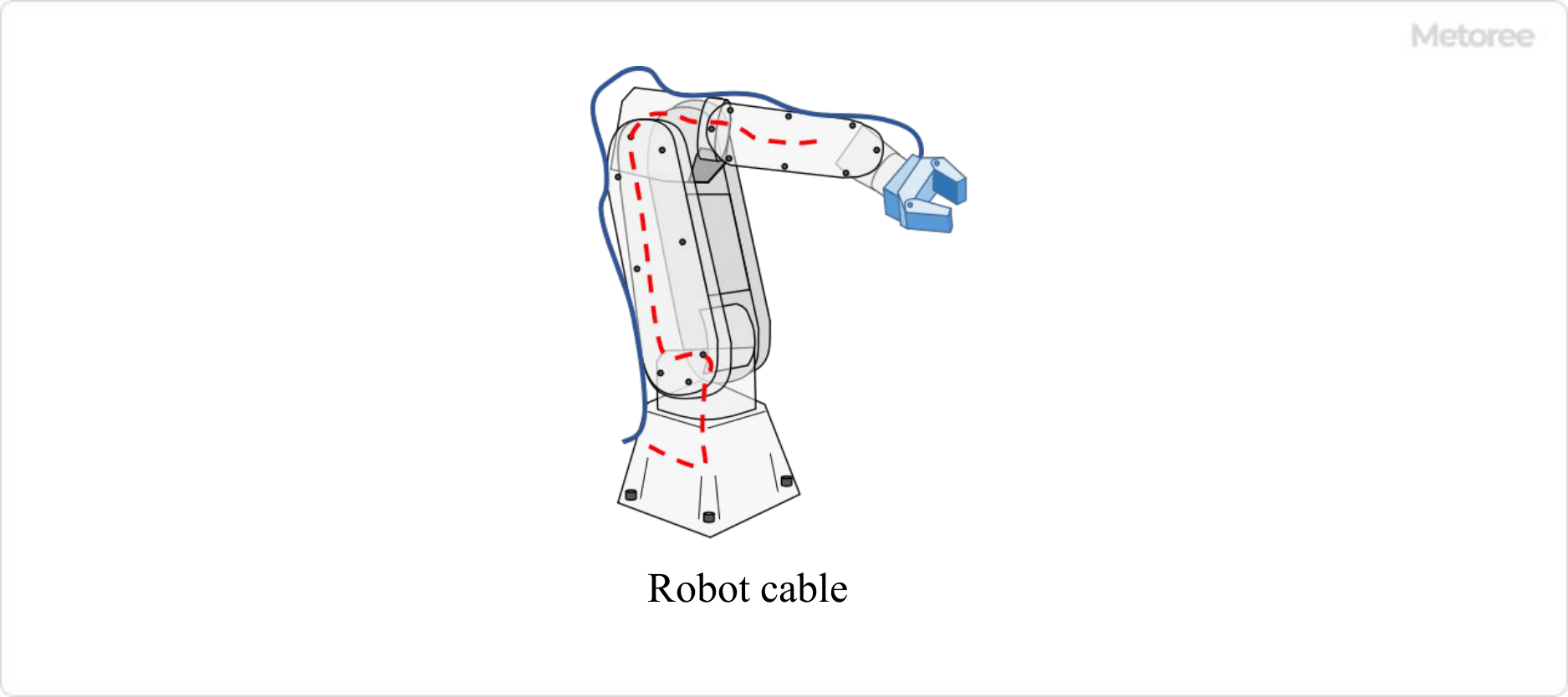
Figure 1. Uses of robot cables
Robot cables are used in the part connecting the robot controller to the robot arm (manipulator part) and inside the robot arm. Robot arms are used in a wide range of industries, including automobiles, precision instruments, home appliances, and machine parts. When selecting a product, it is necessary to analyze the degree and number of repetitive bending and twisting that will occur based on the operation of the robot to be used, and purchase a product that satisfies these requirements.
In addition, specifications such as size (diameter and length), current and voltage, signal transmission speed, and noise performance must also be considered.
Principle of Robot Cables
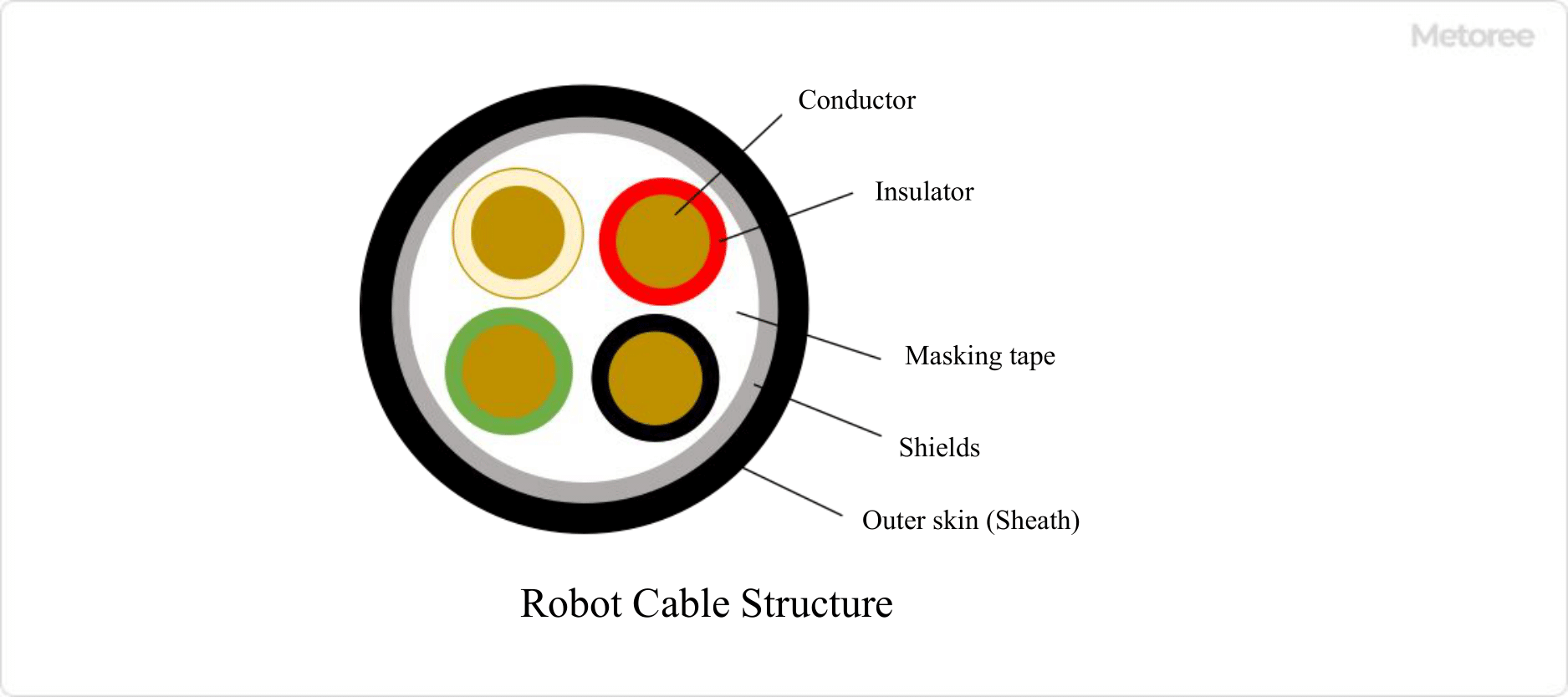
Figure 2. Structure of robot cable
Robot cables consist of multiple bundles of conductors covered with an insulating film, which are surrounded by shielding tape and an outer film.
The components of a 4-conductor robot cable serve the following functions:
- Conductor: Copper wire that carries current and signals.
- Insulator: An insulating film that prevents current flowing in a conductor from leaking out.
- Shielding tape: Tape that binds each individual wire.
- Shield: The part that protects from external noise and is a jacket of copper or aluminum.
- Outer skin (sheath): An outer film that protects the cable from trauma and oil.
The robot cable is connected to the robot controller at one end and to the operating part of the robot at the other end. The robot is operated by transmitting signals and current from the robot controller to the robot.
Since the robot arm frequently bends as it moves, fatigue strength and abrasion resistance are highly demanded. Durable materials (such as PVC) are used to increase fatigue strength and specially treated vinyl or fluororesin coatings are used to increase abrasion resistance.
Other Information on Robot Cables
1. Robot Cable Standards
Robot cable standards vary from country to country, and robot cable manufacturers adhere to standards specific to each country.
The following are examples of standards for robot cables in different countries.
Japan
PSE is a standard that conforms to the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (PSE) and JIS/JCS standards, which specify the insulation and flame resistance of electric cables, etc. JIS/JCS standards aim to standardize cable products.
China
The China Compulsory Certification (CCC) standard is a certification standard for safety, EMC, and environmental protection for products sold in China. This CCC is mandatory in order to sell products in China.
EU
The CE marking is a standard that, once obtained, allows the product to be sold in a total of 31 countries (27 EU member countries and 4 EFTA member countries).
Germany
The TÜV certification (TÜV) is a product safety standard established by TÜV Rheinland, a private German company.
America
UL certification is a product safety standard established by the Underwriters Laboratories Inc. Although acquisition itself is optional, most products sold in the U.S. have acquired this certification, so it is virtually mandatory.
Canada
CSA certification is a product standard established by The Canadian Standard Association. As in the US, obtaining CSA certification is voluntary, but for operational purposes, products cannot be sold unless they are CSA certified.
2. Measures to Prevent Robot Cable Breakage
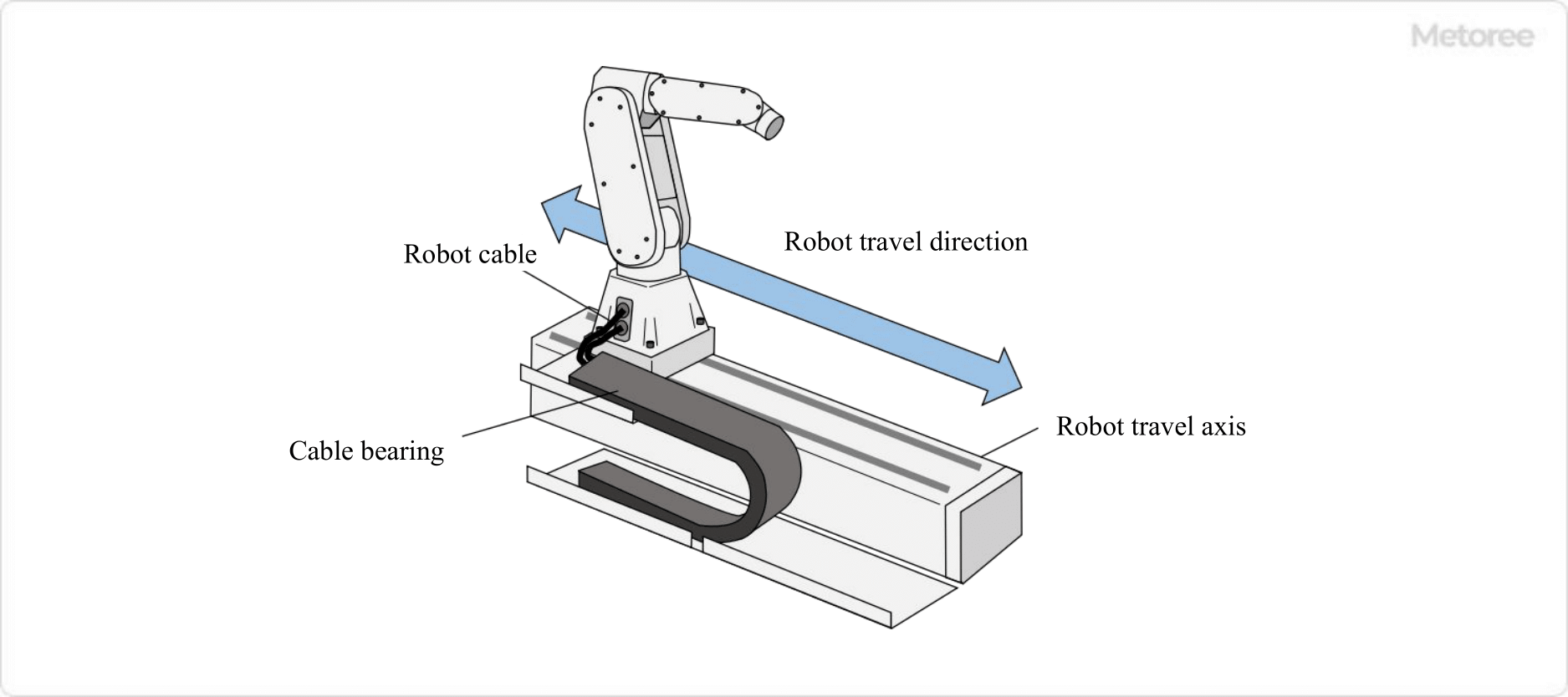
Figure 3. Measures to prevent robot cable breakage
When a robot is installed on a robot traveling axis, there may be cases where the cable gets caught in the moving parts of the traveling axis and breaks.
As a countermeasure, a cableveyor is installed to protect robot cables. Cableveyors are like racks that hold robot cables and air hoses. This ensures that the cables and hoses between the moving equipment and the fixed end are supported and guided, preventing them from becoming entangled in moving parts. Cableveyor bends are designed to bend only in one direction at a fixed radius.