What Is High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipment?
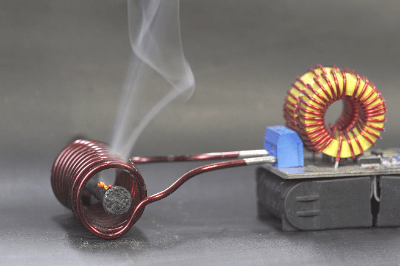 A high-frequency induction heating device is a device that heats by high-frequency induction.
A high-frequency induction heating device is a device that heats by high-frequency induction.
When alternating current is passed through a coil containing a metal body, a magnetic field is generated by the current flowing in the coil, causing induction loss, or hysteresis loss, which generates heat. At the same time, eddy currents, or eddy currents, are generated in the changing magnetic field due to electromagnetic induction. These eddy currents generate Joule heat, which causes eddy current losses.
High-frequency induction heating equipment utilizes the two heating principles of hysteresis loss and eddy current loss. The energy supplied to the object to be heated per unit area and unit time is large, making high-speed heating possible.
Uses of High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipments
High-frequency induction heating is often used for melting, quenching, and brazing of metals because it can heat conductors such as metals without contact. A familiar example is the induction cooktop. Other applications include resins, wood, textiles, food, and medicine.
In the case of thermoplastic resins, induction heating can be used to weld resins while pressing them in a mold. In the case of food production, high-frequency induction heating equipment can be incorporated into factory lines to defrost food products rapidly when processing large quantities of food products.
In the medical field, high-frequency induction heating methods are also used in the development of cancer thermotherapy and other treatments.
Principle of High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipments
High-frequency induction heating is a method of heating an object using electromagnetic induction. It can be classified as a direct heating method or an indirect heating method, depending on whether the object to be heated is heated by passing an electric current directly through it or through a conductive container.
1. Direct Heating Method
The law of electromagnetic induction states that when an alternating current is applied to a coil, a magnetic flux is generated that passes through its center and surrounds the outside. Eddy currents are generated in the metal to prevent this magnetic flux from changing.
Depending on the magnitude of these eddy currents and the electrical resistance of the metal, Joule heat is generated in the metal. In the direct heating method, the object to be heated can be directly heated by generating eddy currents directly in the metal in this way.
2. Indirect Heating Method
The indirect heating method is used to heat insulators such as ceramics, which cannot generate eddy currents in the object to be heated. Therefore, indirect heating is possible by placing the object to be heated in a conductive container and heating the container.
To increase heating efficiency, the gap between the external shape of the object to be heated and the heating coil is reduced to increase the flux density transmitted. Furthermore, the heating is done by controlling the frequency of the AC power source between tens of Hz and hundreds of kHz.
Other Information on High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipment
1. Advantages of High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipment
Uniform Heating
The heat is generated by resistance heating against eddy currents generated by electromagnetic induction, so the heated object is uniformly heated from the inside.
Rapid Heating
By controlling the transmitter, high-frequency waves can be applied instantaneously to the object to be heated, and since the heating is internally self-heated, rapid heating is possible. Compared to heating furnaces that apply heat externally, this system is superior in productivity and requires no standby heating, making it a low-cost production method.
Selective Heating
Even for composite materials such as aluminum alloy and steel clad steel, only the portion of the material with high electrical resistivity can be selectively heated.
High Energy Efficiency
In general heating furnaces, external heating is done by combustion or heating elements, resulting in energy loss due to unnecessary heating of not only the object to be heated but also the furnace components and atmosphere. With high-frequency induction heating equipment, only the object to be heat-treated is heated by self-heating, thus eliminating waste and enabling heat treatment with high energy efficiency.
2. Disadvantages of High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipment
Expensive Capital Investment
High-frequency induction heating has the disadvantage that the initial capital investment is expensive because high-frequency induction heating equipment requires expensive high-frequency power supplies and control devices, as well as equipment to prevent electromagnetic radiation leakage to the surrounding environment.
Low Shape Selectivity
If the electric field of the object to be heated is non-uniform, the heat generation itself will also be non-uniform, resulting in uneven temperatures, which may lead to problems such as melting in the worst case. Therefore, the object to be heated should have a highly symmetrical shape, such as a cylinder. It is difficult to heat complexly shaped objects, such as square timbers or gears, evenly.
Individual and Partial Heating
High-frequency induction heating is a method of heating the whole or only a part of the object to be heated by means of an arbitrarily shaped coil designed to heat the object uniformly. For this reason, it is basically a one-piece flow process, and thus cannot perform batch-type mass simultaneous processing like external heating. Depending on the product and production conditions, this method has the disadvantage of reduced productivity.