What Is Allene?
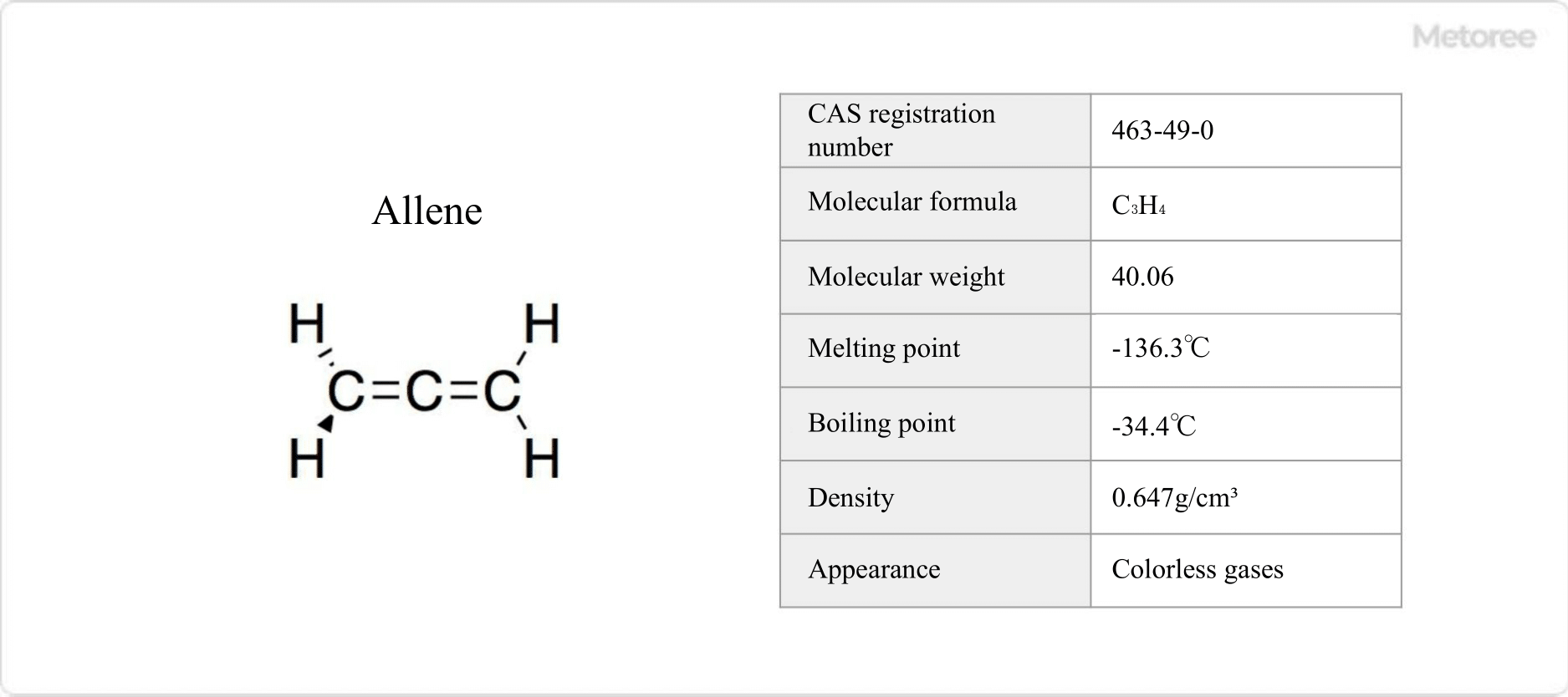
Figure 1. Basic Information on Allene
Allene is an organic compound with a structure consisting of three carbon atoms joined on a linear chain by two double bonds.
These compounds are collectively called allenes. The compound with the most basic structure among allenes is propadiene. Propadiene is sometimes referred to as allene.
Propadiene can be synthesized by the action of zinc powder on an ethanol solution of 2,3-dibromopropene or 2,3-dichloropropene. On the other hand, when propadiene absorbs sulfuric acid and is distilled with water, it becomes acetone.
Uses of Allene
Propadiene, “allene” in the narrow sense, is used as a component of MAPP gas MAPP gas is a mixture of propadiene and methylacetylene MAPP gas is used for soldering and welding. It is safe and easy to transport but is not cost-effective.
Compounds classified as “allene” in the broad sense of the word are not used industrially. However, allene is highly reactive and can undergo a variety of addition reactions, making it a promising candidate for use in useful chemical reactions. Allene is characterized by its axial chirality.
Properties of Allene
The chemical properties of allenes differ significantly from those of common alkenes. Allene is very unstable when compared to conjugated and isolated dienes. The C-H bonds in allene are weaker and more acidic than the C-H bonds in vinyl groups.
Allene undergoes [2+2] and [4+2] cycloaddition reactions. Formal cycloaddition reactions proceed when transition metal catalysts are used.
Propadiene, the most basic structure of allene, is a colorless gas with a sweet odor. It has a melting point of -136.3°C and a boiling point of -34.4°C. It is virtually insoluble in water. It decomposes easily but is highly stable and is used as a welding fuel along with methylacetylene.
Structure of Allene
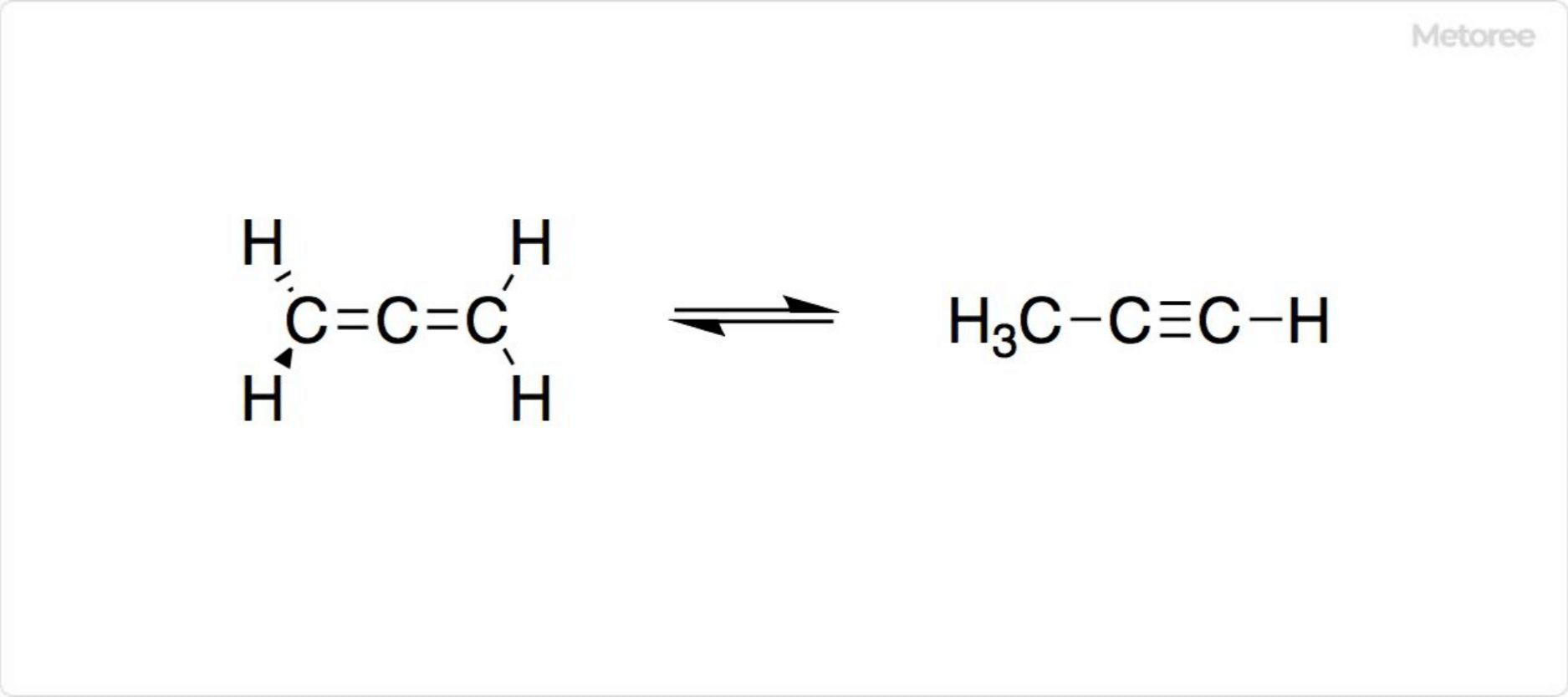
Figure 2. Synthesis of Allene
A structure with two or more consecutive double bonds, as in allene, is called an integrated double bond. The chemical formula is R2C=C=CR2. The name for a compound with three or more double bonds in a row is cumulene. Substituents such as R2C=C=CR–, where R is an alkyl group of allene, are called allenyl groups.
The most basic structure of allene, propadiene, has the chemical formula H2C=C=CH2. Propadiene exists in equilibrium with methylacetylene, which has the chemical formula H3C-C3≡CH. Special synthetic methods are often required for the synthesis of allene. However, industrially, propadiene is synthesized from a mixture with methylacetylene.
Other Information on Allene
1. Geometric Structure of Allene
The central carbon atom of allene has two sigma and two pi bonds. The two terminal carbon atoms have sp2 hybrid orbitals. The three carbon atoms form a linear structure with a bond angle of 180°. The two terminal carbon atoms form a planar structure, and each plane is twisted 90° in configuration.
2. Molecular Symmetry of Allene
The allene molecule is often compared to a two-bladed propeller. That is, allene has four substituents, and from two different terminal CH2 planes through the central carbon atom, there are two 2-fold rotational symmetry axes C2 inclined at 45°.
There is a third two-fold rotational symmetry axis along the C=C=C bond axis, and the two CH2 planes are both mirror symmetry planes. Based on the above, the symmetry of the allene molecule belongs to the point group D2d, and allene without substituents is a nonpolar molecule with no total dipole moment.
3. Isomers of Allene
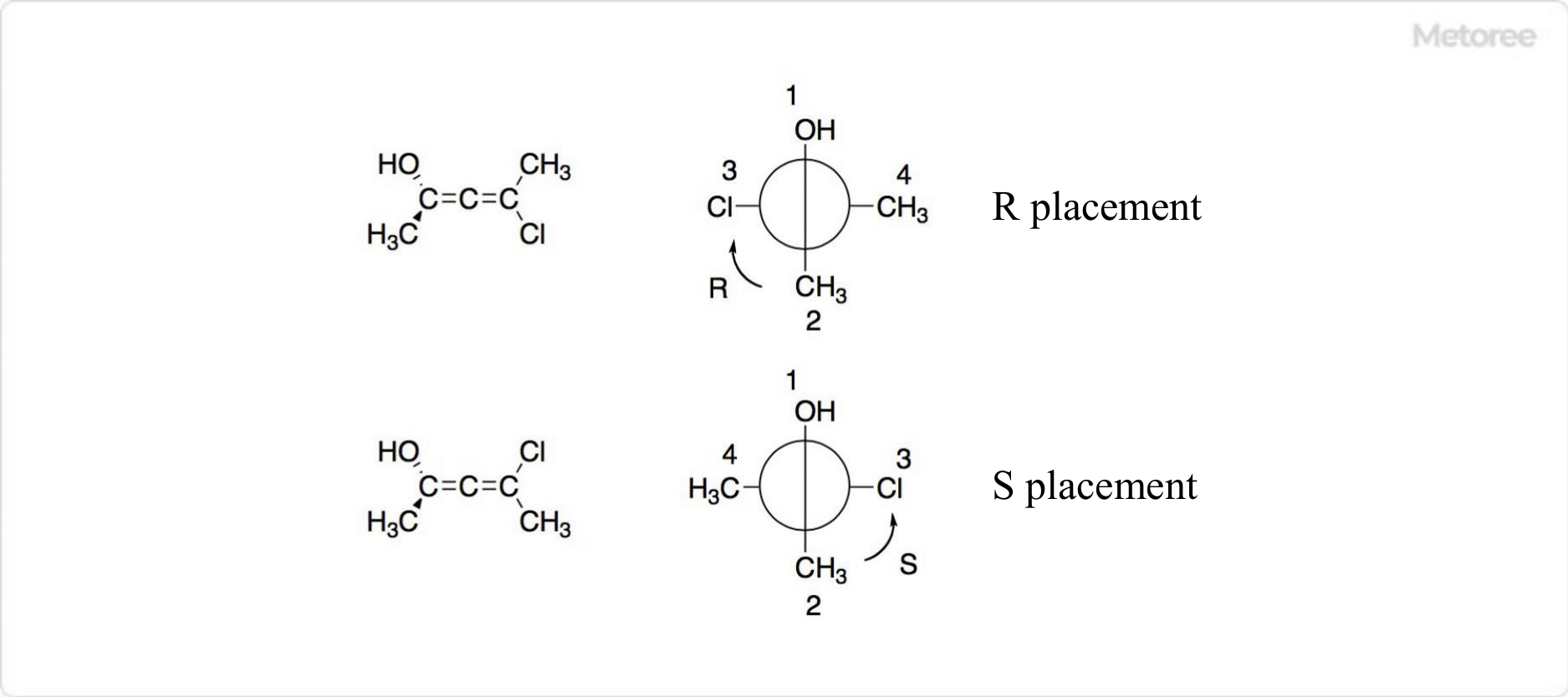
Figure 3. Isomers of Allene
Derivatives in which two carbon atoms of the allene molecule are bonded to two different substituents have mirror-image isomers. The R and S configurations can be determined by the priority of the substituents when the allene molecule is viewed along its axis. The front side is preferred over the back side, which is determined by the relative arrangement of the front and back sides.
Thus, allene has unusual optical properties and is used as a building block in the synthesis of organic materials.