What Is Ethyl Bromide?
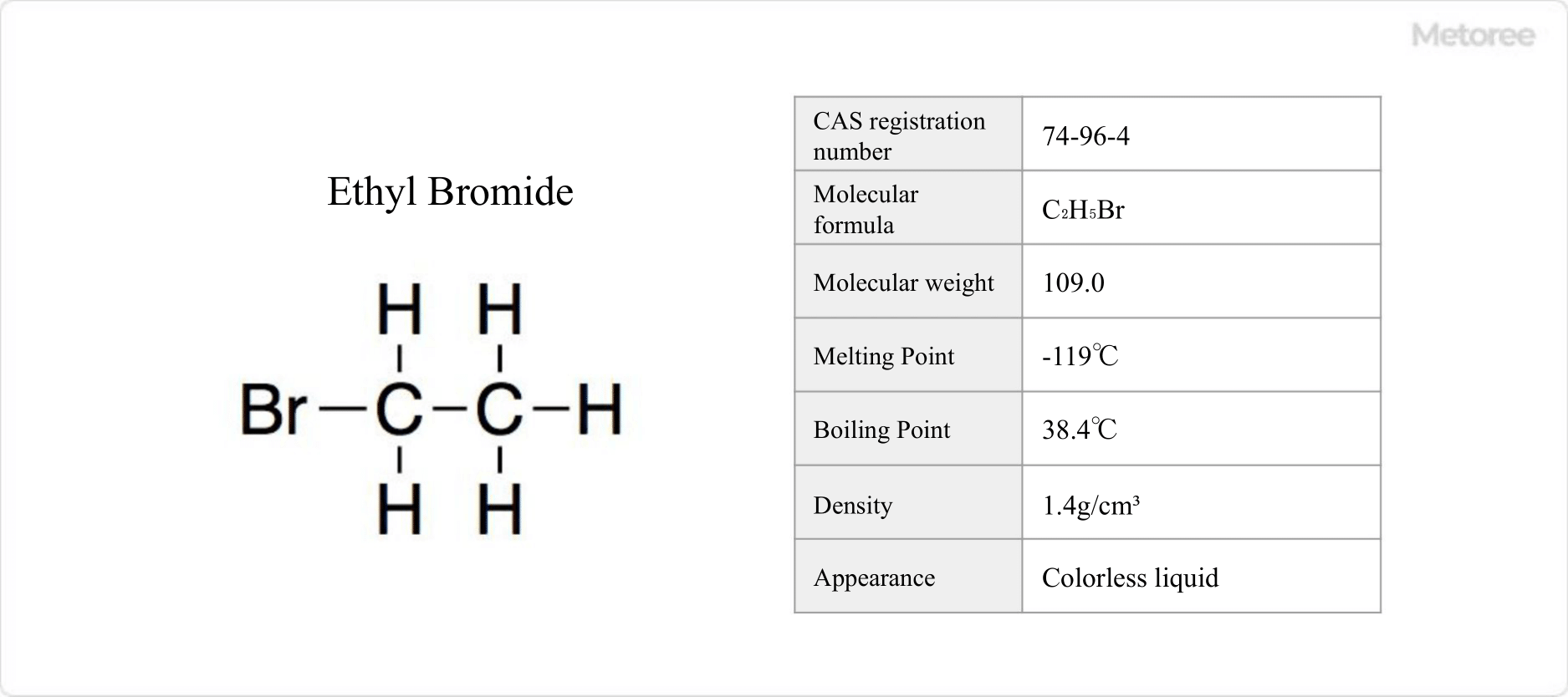
Figure 1. Basic Information on Ethyl Bromide
Ethyl bromide, also known as bromoethane, is a halogenated hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C2H5Br.
It is classified under various laws due to its hazardous and toxic nature. Under the Industrial Safety and Health Law, it is labeled as hazardous and toxic, needing notification, and classified as a flammable substance. The Labor Standards Law identifies it as a disease-causing chemical substance, while the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law and the Fire Service Law categorize it as a deleterious substance and a hazardous material, respectively. Protective equipment is essential when handling ethyl bromide.
Uses of Ethyl Bromide
As an ethylating agent in organic synthesis, ethyl bromide is used to create ethyl esters from carboxylates and synthesize ethylamine by ethylating amines. It also serves as a raw material for the indispensable Grignard reagent in organic synthesis and is utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing, including anesthetics.
Properties of Ethyl Bromide
With a melting point of -119°C and a boiling point of 38.4°C, ethyl bromide is a colorless, volatile liquid with an ethereal odor. It is highly flammable, with a flash point below -2°C, and has an explosive range of 6.8-8.0%. Insoluble in water, it dissolves slightly at 20°C and is soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and benzene. Exposure to ethyl bromide can cause severe irritation and poisoning symptoms upon inhalation, skin contact, or eye exposure.
Structure of Ethyl Bromide
Abbreviated as EtBr, ethyl bromide is formed by replacing one hydrogen atom in ethane with a bromine atom. It has a molecular weight of 109.0 g/mol and a density of 1.4 g/cm3.
Other Information on Ethyl Bromide
1. Synthesis of Ethyl Bromide
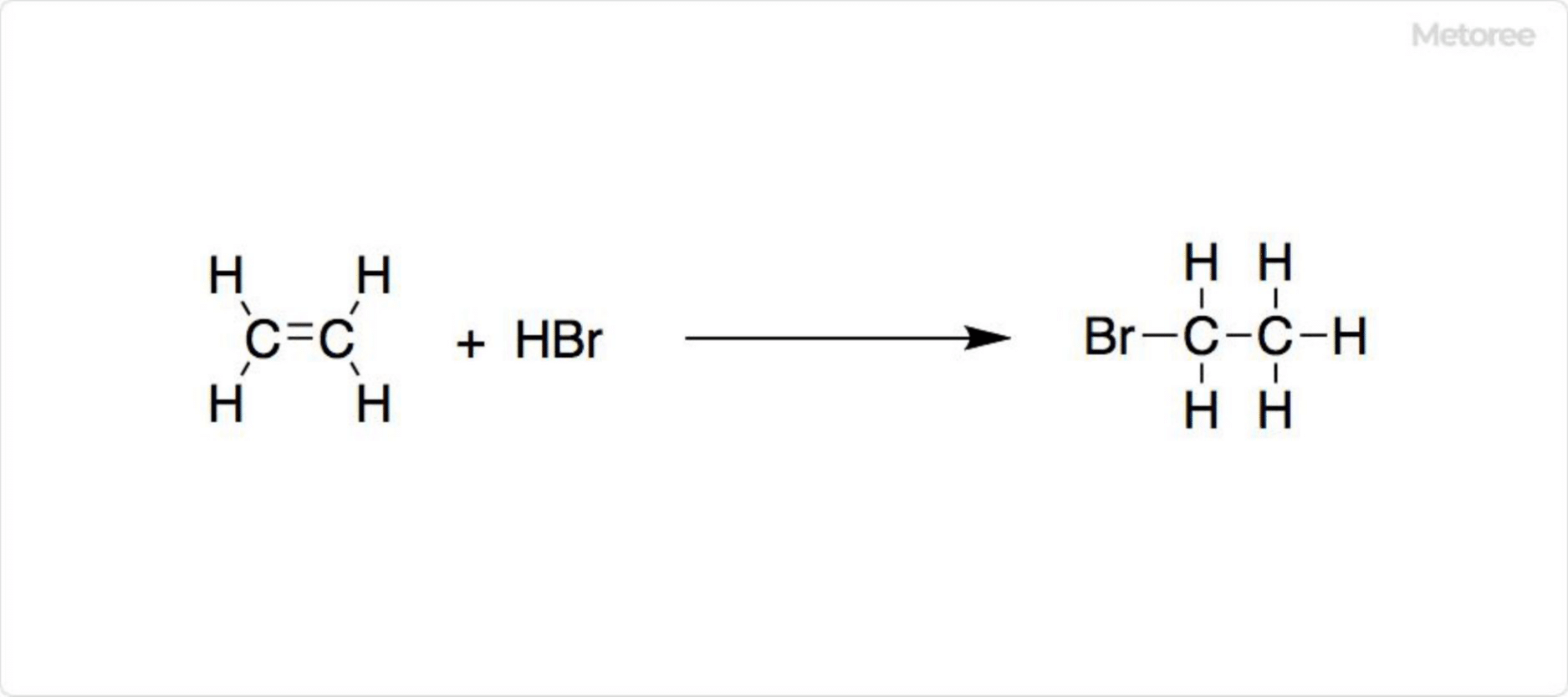
Figure 2. Synthesis of Ethyl Bromide
Synthesis typically involves the addition of hydrogen bromide to ethylene, or distillation of ethanol with hydrobromic acid and a small amount of sulfuric acid, also producing diethyl ether as a byproduct. Alternatively, ethyl bromide can be produced from ethanol using thionyl bromide (SOBr2) or phosphorus tribromide (PBr3).
2. Reaction of Ethyl Bromide
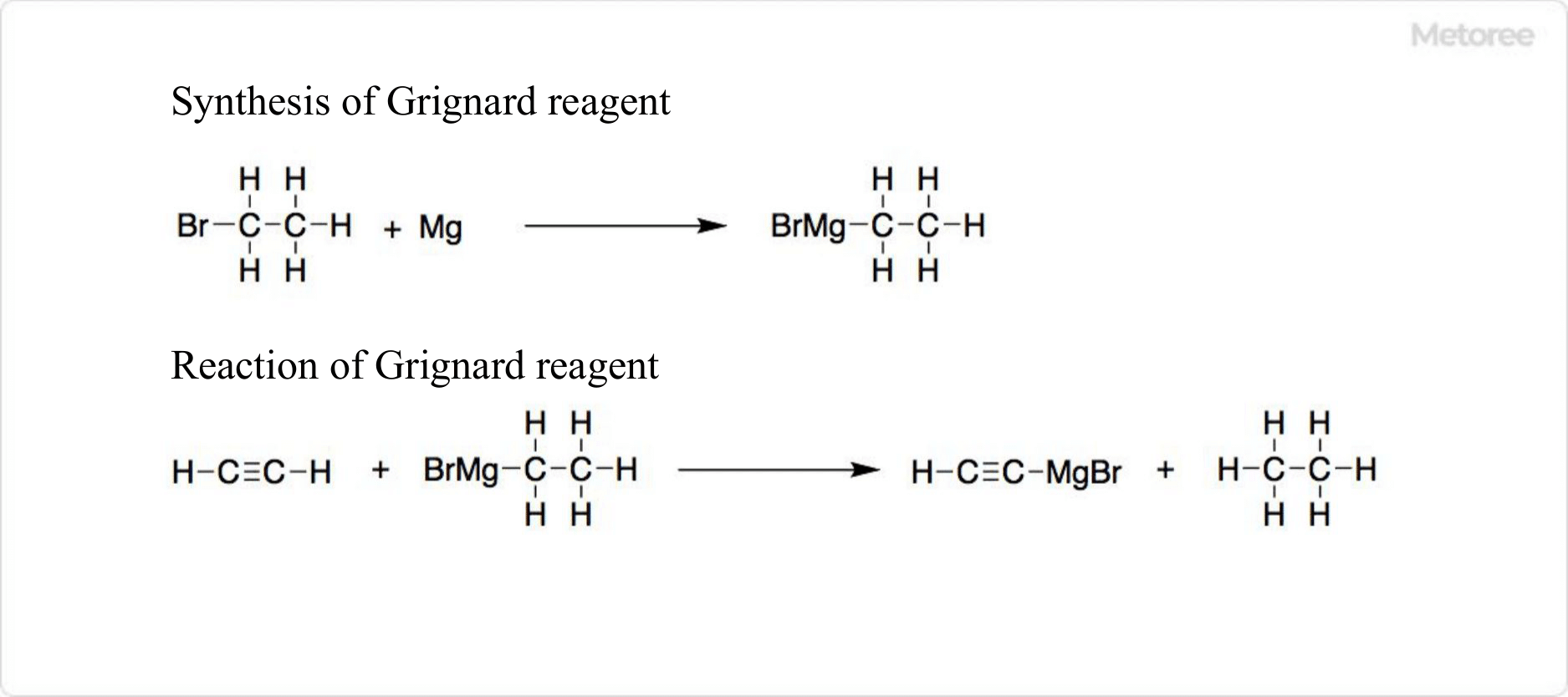
Figure 3. Reaction of Ethyl Bromide
Ethyl bromide reacts with alkali to form ethylene and is a cost-effective reagent for preparing Grignard reagents. In organic chemistry, it serves as a superior alkylating agent compared to ethyl chloride, facilitating the synthesis of ethyl esters, ethylation of pseudo-carbanions, and production of ethylisothiouronium salts and ethylamine.