What Is Cholic Acid?
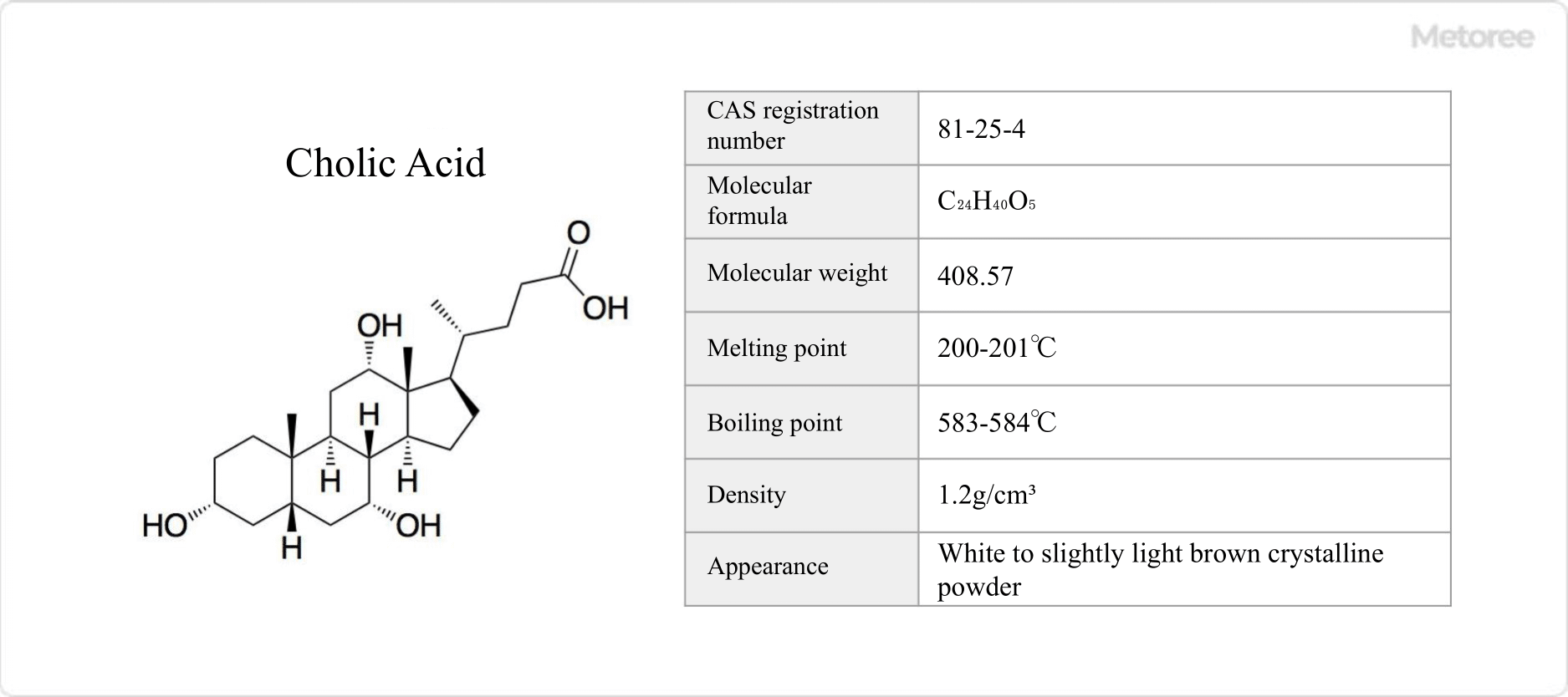
Figure 1. Basic information on cholic acid
Cholic Acid is a bile acid with a chemical formula of C24H40O5. It is typical of steroids.
The liver can synthesize cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, the primary bile, from cholesterol. They also form conjugates with the amino acids glycine and taurine, and are secreted into the duodenum as bile components.
The secreted primary bile acids can be released from glycine and taurine by the action of intestinal bacteria in the small intestine. They are then converted to deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, called secondary bile acids, which are returned to the liver from the terminal end of the small intestine.
Uses of Cholic Acid
Animal bile has been used in herbal medicine since ancient times. Among them, bear bile, made from dried bear bile, is said to be effective for pain near the gallbladder, one of the three most painful conditions. Its main ingredient is ursodeoxycholic acid, a secondary bile acid.
Cholic acid is used as a medicine. Ursodeoxycholic acid is used as a gastrointestinal drug, while chenodeoxycholic acid is used as a drug therapy for cholesterol-based gallstone dissolution and as a gastrointestinal drug.
Properties of Cholic Acid
Cholic Acid is slightly soluble in water. Its melting point is 200-201°C and boiling point is 583-584°C.
When recrystallized with dilute acetic acid, it produces a plate-like crystal with one molecule of crystalline water. When recrystallized from alcohol, crystals with a single molecule of alcohol are produced; heating to 130°C removes the crystalline solvent and can produce an anhydride.
It emulsifies water-insoluble substances such as fats in the intestinal tract, thereby aiding digestion and absorption and facilitating enzymatic action. It is present in the bile of most vertebrates in peptide bonds with glycine or taurine.
Structure of Cholic Acid
Cholic Acid is a steroid that forms amides with amino acids and is found in many organisms. Steroids are naturally occurring triterpenoids. Terpenoids are derivatives of isoprene-based hydrocarbons, terpenes, that have functional groups such as hydroxy and carbonyl groups.
Cholic Acid is also called 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid. Its molecular weight is 408.579 g/mol and its density is 1.2 g/cm3.
Other Information on Cholic Acid
1. Glycolic Acid in the Body
Cholic Acid is usually condensed with amino acids and exists as a conjugated bile acid. In humans, the majority are glycocholic acid and taurocholic acid. Cholic Acid in its raw form can cause tissue damage.
2. Characteristics of Cholic Acid
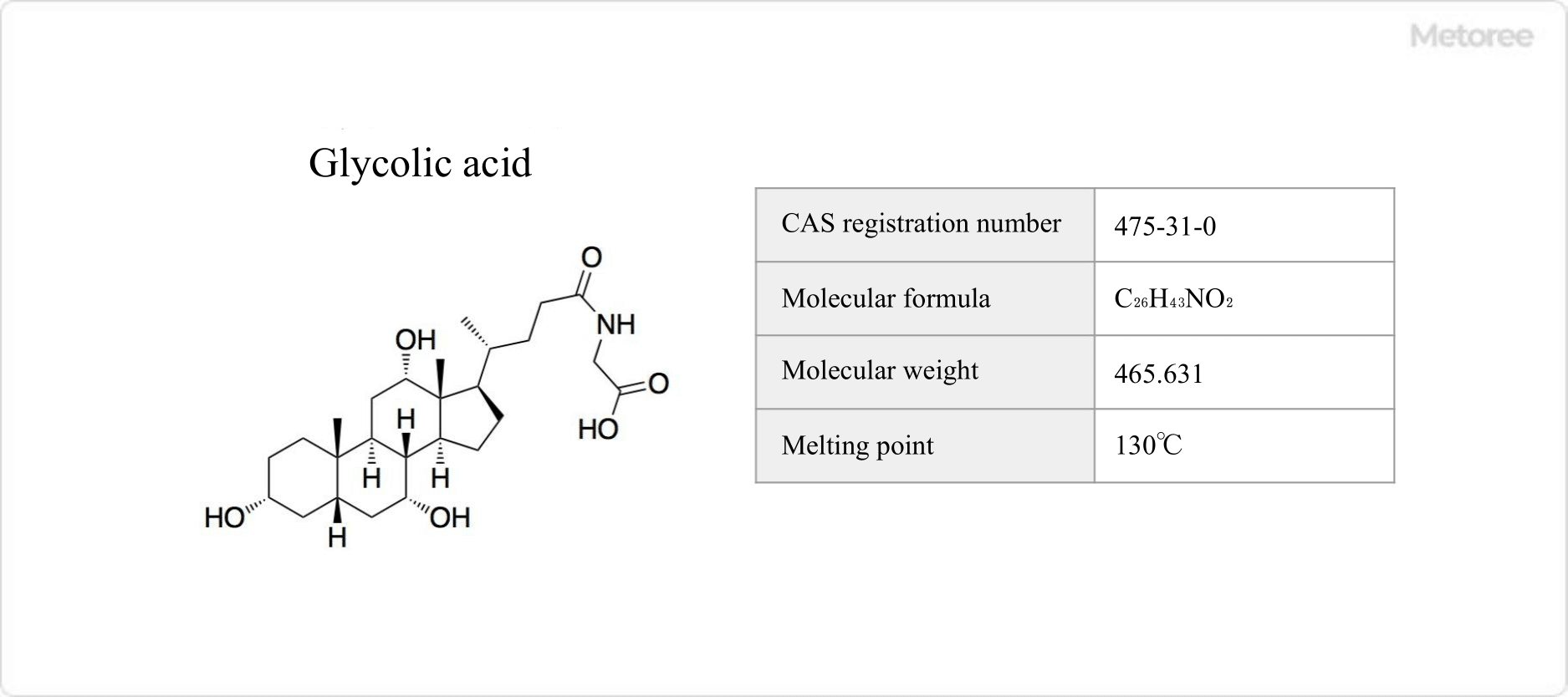
Figure 2. Basic information on glycolic acid
Glycolic Acid is a conjugated bile acid that is a condensation of cholic acid and glycine. It accounts for about two-thirds of human bile acids and is a transparent bile acid capable of emulsifying fats.
It is biosynthesized by the reaction of glycine and choryl CoA. Its chemical formula is C26H43NO6, its molecular weight is 465.6 g/mol, and its melting point is 130°C. It is a bile acid of mammals and also exists transformed to its sodium salt.
3. Characteristics of Taurocholic Acid
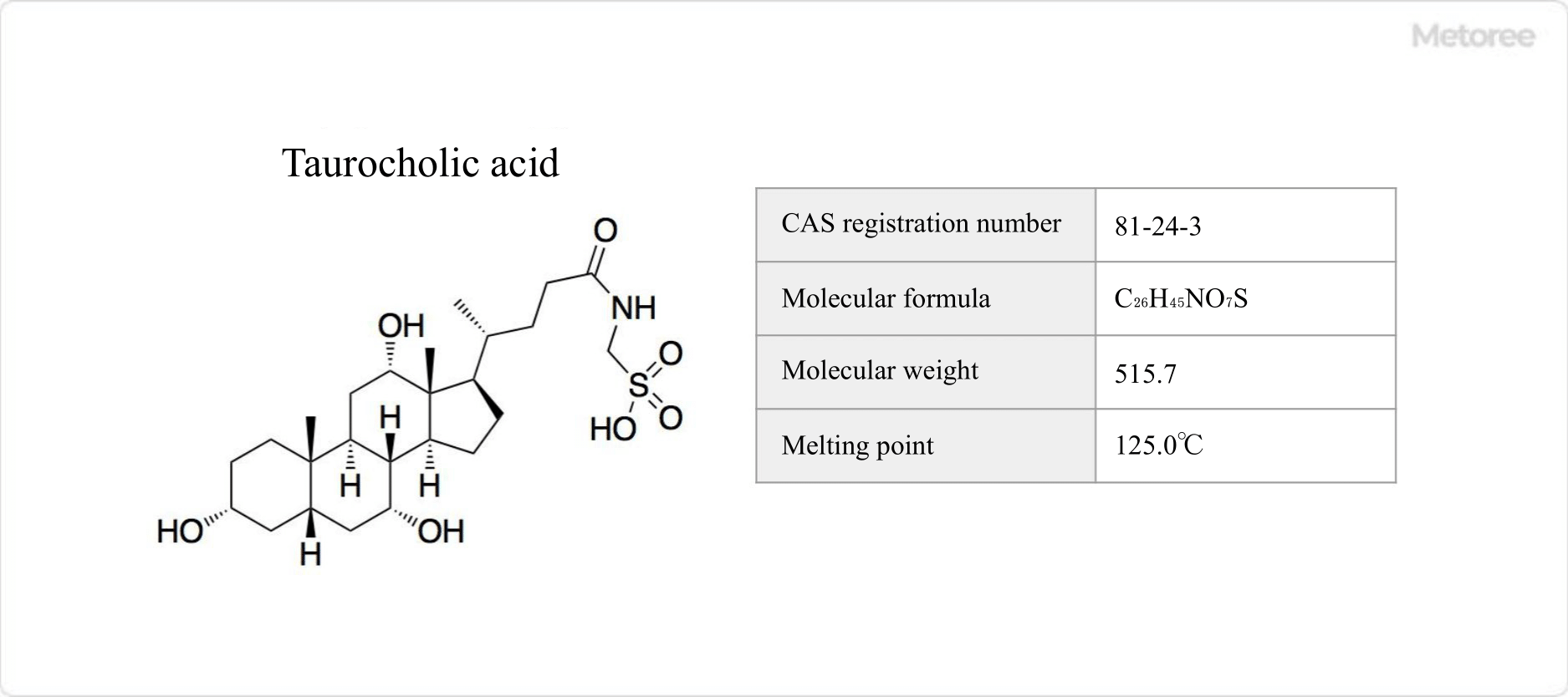
Figure 3. Basic information on taurocholic acid
Taurocholic acid is a conjugated bile acid that is a condensation of cholic acid and taurine. It is a clear yellow bile acid with fusible properties and accounts for about one-third of human bile acids. It is biosynthesized by the reaction of taurine and cholic acid. Its chemical formula is C26H45NO7S, its molecular weight is 515.7 g/mol, and its melting point is 125.0°C.
Medicinally, it is used as a cholecystokinin and diuretic. Commercially, it can be produced from bovine bile, a byproduct of the meat industry. The 50% lethal dose (LD50) in newborn rats is 380 mg/kg.