What Is a Plastic Glove?
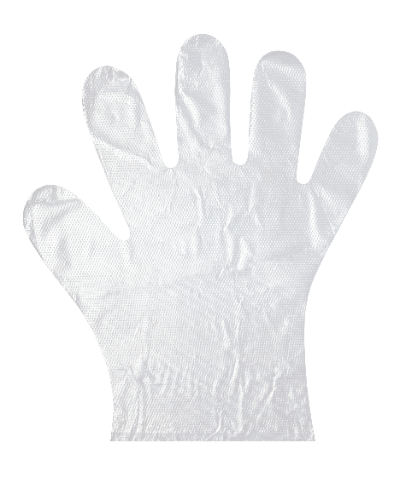

Plastic gloves, commonly known as PVC gloves, are a type of disposable gloves, alongside other varieties such as latex gloves from natural rubber, nitrile gloves from synthetic rubber, and gloves made from polyvinyl chloride. These gloves have found widespread use across various industries, including medical, caregiving, precision component manufacturing, water-related industries, and oil-handling workplaces.
Since the global spread of COVID-19 in 2020, the demand for disposable gloves has surged, becoming increasingly common in customer service roles in restaurants and grocery stores to prevent virus transmission.
Each glove type has distinct features, including appearance, elasticity, chemical resistance, heat resistance, and cost, influencing their suitability for different tasks.
Applications of Plastic Gloves
While plastic gloves are less elastic compared to latex or nitrile gloves, they stand out for their chemical resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. These gloves are easily removable from the wrist, avoiding contact with contaminated fingertips, making them ideal for caregiving, childcare, nursing, cleaning, beauty salons, metal processing, construction, and other tasks.
Manufacturing of Plastic Gloves
Plastic, a petroleum-derived product, is created from naphtha, a component separated during crude oil refining. Naphtha undergoes further processing to produce polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene, which form the basis of plastic. Additives in these polymers provide specific characteristics like softness, breakage resistance, and color.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), used for plastic gloves, is also utilized in making electrical cords and films. Gloves are produced through dip molding, where liquid PVC molds are formed, dried, and undergo various post-processing steps.
China, a major producer, saw a significant increase in glove demand during the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to shortages in countries like Japan due to decreased factory operations in China.
Selecting Plastic Gloves
When choosing plastic gloves, consider factors such as thickness, length, wrist closure, and the task at hand. Thin gloves are ideal for delicate tasks, while thicker ones offer better durability and abrasion resistance. Options with or without cornstarch powder are available, depending on preference for powder contamination. It’s important to note that PVC dissolves in organic solvents, which can be a limitation in certain environments.