What Is Cloth Tape?
Cloth tape, constructed from durable materials such as polyethylene and polyester woven into a robust fabric, offers exceptional strength and minimal lint production during cutting. Its hand-tearable nature and ease of use make it an efficient choice for various applications, including packaging and protective covering for exterior walls and concrete surfaces.
Available in a range of base materials, from standard polyethylene cloth to specialized laminated and glass cloths, cloth tape comes in various adhesive strengths and colors. Selection should be based on the specific requirements of the intended use.
Uses of Cloth Tape
Cloth tape serves a broad spectrum of applications, from packaging to repair and reinforcement, thanks to their reinforced structure provided by the interwoven fibers.
1. Packaging Industry
Utilized for sealing boxes and packages, cloth tape’s crosshatch pattern enhances package integrity, ensuring secure transport and storage.
2. Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, cloth tape offers a quick-fix solution for repairing machinery or equipment parts, supporting both temporary fixes and more permanent repairs.
3. Crafts and DIY Projects
For craft and DIY enthusiasts, cloth tape is ideal for binding and reinforcing a variety of materials, ensuring durability and stability in creative projects.
4. Household Use
From book repair to furniture restoration, cloth tape is a versatile tool for general home maintenance, offering strong adhesion and long-lasting results.
Features of Cloth Tapes
The crosshatch pattern on cloth tape not only enhances its tensile strength but also ensures even distribution of stress, making it highly reliable for various applications. This pattern, coupled with a durable adhesive, ensures that the tape remains securely in place.
Types of Cloth Tape
- Reinforcement Tape – Designed for heavy-duty repair and reinforcement, this tape is ideal for a wide range of applications, from paper and plastic repairs to strengthening household and industrial items.
- Packaging Tape – Its strong bond and durability make cloth tape an excellent choice for packaging, especially for heavy or irregularly shaped items.
- Waterproof Tape – Water-resistant cloth tape is perfect for outdoor use or in moist environments, providing reliable sealing and repair solutions.
- High-Temperature Tape – Suitable for applications requiring resistance to high temperatures, this tape is used in repair and sealing tasks sensitive to heat.
- Fabric Tape – Specifically designed for textiles, fabric tape is used in clothing and upholstery repairs, customization, and reinforcement.
- Double-Sided Tape – Offering adhesive on both sides, double-sided cloth tape is used for mounting, decoration, and flooring applications, ensuring stable adherence.
Material Considerations for Cloth Tapes
Typically made from strong synthetic fibers or polymers, cloth tapes are engineered for high tensile strength and versatility, capable of meeting the demands of various applications through a combination of durable materials and effective adhesives.
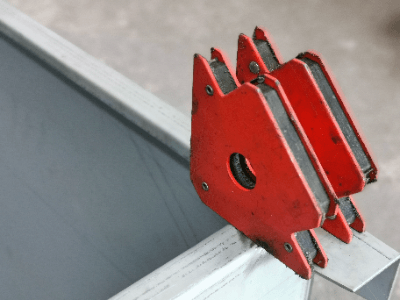 A welding magnet, also known as a magnet holder or mag hold, is a jig equipped with a magnet to hold materials in the correct position during welding. It is particularly useful when handling heavy materials or performing detailed work where one-handed operation may lead to instability, burns, or pinching.
A welding magnet, also known as a magnet holder or mag hold, is a jig equipped with a magnet to hold materials in the correct position during welding. It is particularly useful when handling heavy materials or performing detailed work where one-handed operation may lead to instability, burns, or pinching.
 A lifting strap, commonly known as a round sling, is a flexible belt device used for lifting and carrying heavy loads. Made from softer materials than other types of slings, such as
A lifting strap, commonly known as a round sling, is a flexible belt device used for lifting and carrying heavy loads. Made from softer materials than other types of slings, such as  A spiral flute tap is a tool used to create threaded holes in materials. Unlike straight-groove taps, which have blades extending in all directions, spiral flute taps feature spiral-shaped blades. This design enhances chip ejection during
A spiral flute tap is a tool used to create threaded holes in materials. Unlike straight-groove taps, which have blades extending in all directions, spiral flute taps feature spiral-shaped blades. This design enhances chip ejection during