What Is Ethyl Acetoacetate?
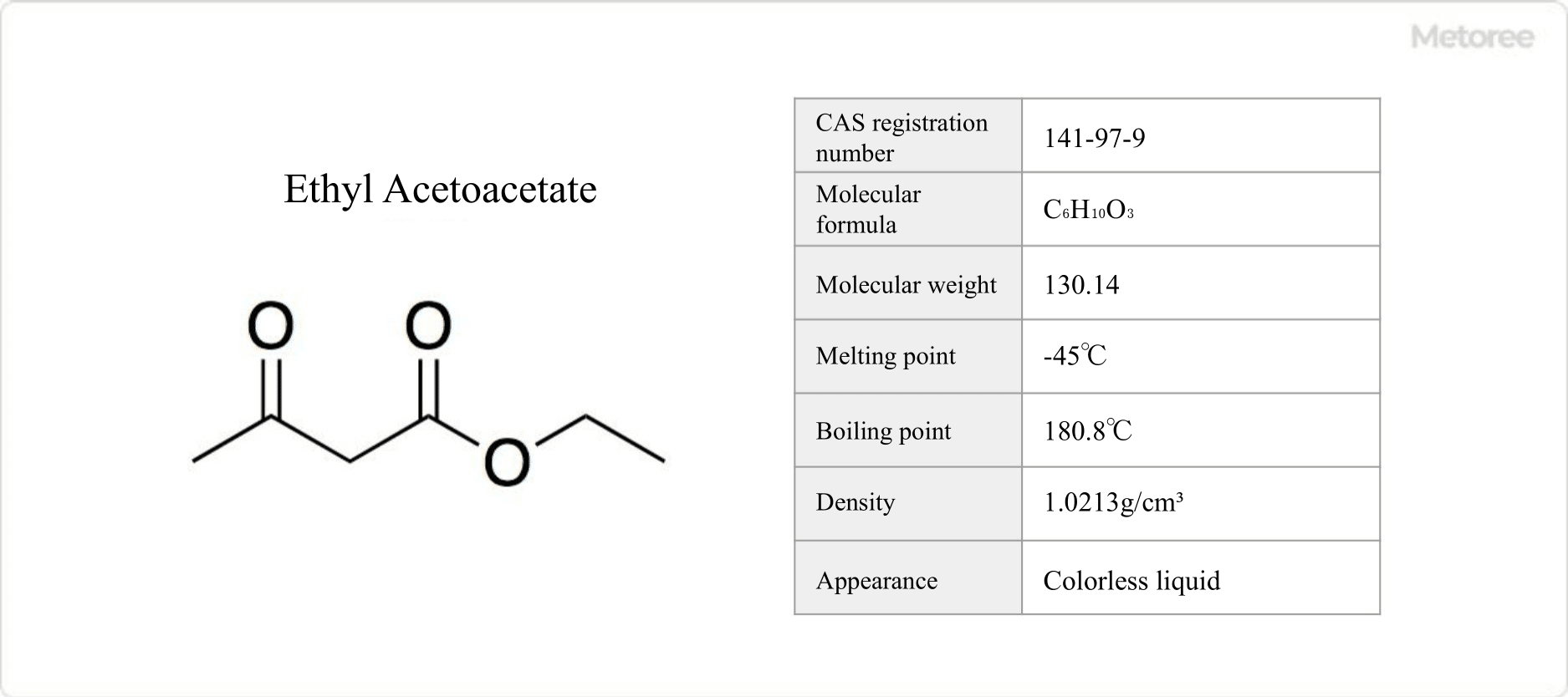
Figure 1. Basic Information on Ethyl Acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate is the ethyl ester of acetoacetate, with the chemical formula C6H10O3. Also known as ethyl 3-oxobutanoate, it is a colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic fruity odor. It is classified as a Class 4 Hazardous Substance and a Class 3 Non-Water Soluble Liquid under the Fire Service Law.
The relatively stable carbanion produced by the action of a base on ethyl acetoacetate is often used in carbon-carbon bond formation reactions.
Uses of Ethyl Acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate is more reactive than other esters and is used as a raw material for various organic syntheses. Examples include its use as an intermediate in the manufacture of compounds such as antipyretic analgesics, antimalarials, antibiotics, amino acids, and vitamin B.
It also has a fruity odor and is used as a food flavoring agent and in perfumes. Additionally, it can be used in lacquer paints, dye manufacturing, plastic manufacturing, and as an analytical reagent.
Properties of Ethyl Acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate has a melting point of -45°C, a boiling point of 180.8°C, a flash point of 70°C, and a refractive index of 1.41937 at 20°C. It is soluble in water at 20°C, with 2.86 g dissolving in 100 mL of water. It is extremely soluble in ethanol and acetone.
The hydrogen atom on the methylene moiety at position 2 of ethyl acetoacetate is relatively acidic, with a pKa of 10.7 at 25°C.
Hydrolysis of ethyl acetoacetate with dilute acid or dilute alkali yields carbon dioxide and acetone. However, when reacted with a strong alkali, acetic acid is formed.
Structure of Ethyl Acetoacetate
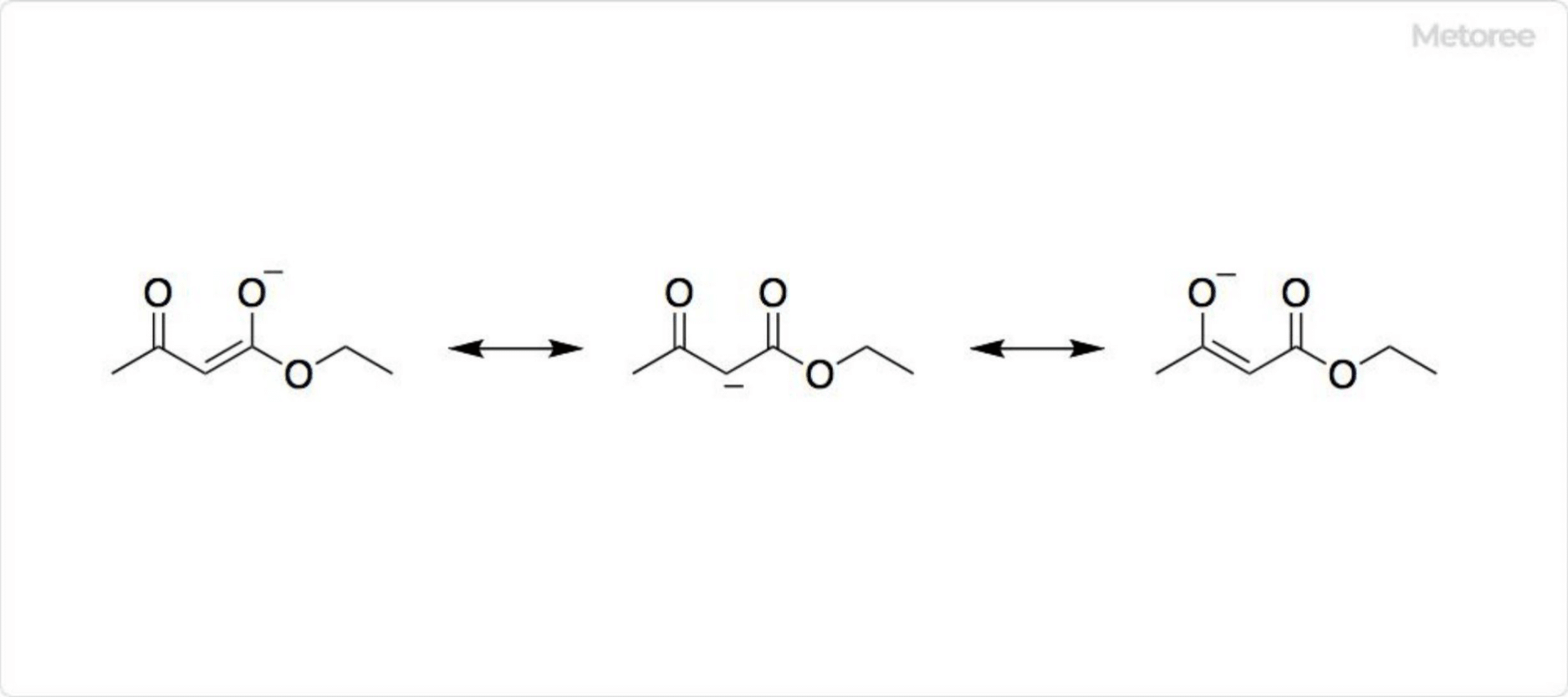
Figure 2. Structure of Ethyl Acetoacetate
The empirical formula of ethyl acetoacetate is CH3COCH2COOC2H5. Its molecular weight is 130.14 g/mol, and its density at 25°C is 1.021 g/cm3.
Ethyl acetoacetate exhibits keto-enol tautomerism; at 33°C, the enol form constitutes 15% of the total.
The carbanion, the conjugate base of ethyl acetoacetate, is in resonance with the two enolate structures, allowing the negative charge to be delocalized and stabilized.
Other Information on Ethyl Acetoacetate
1. Synthesis of Ethyl Acetoacetate
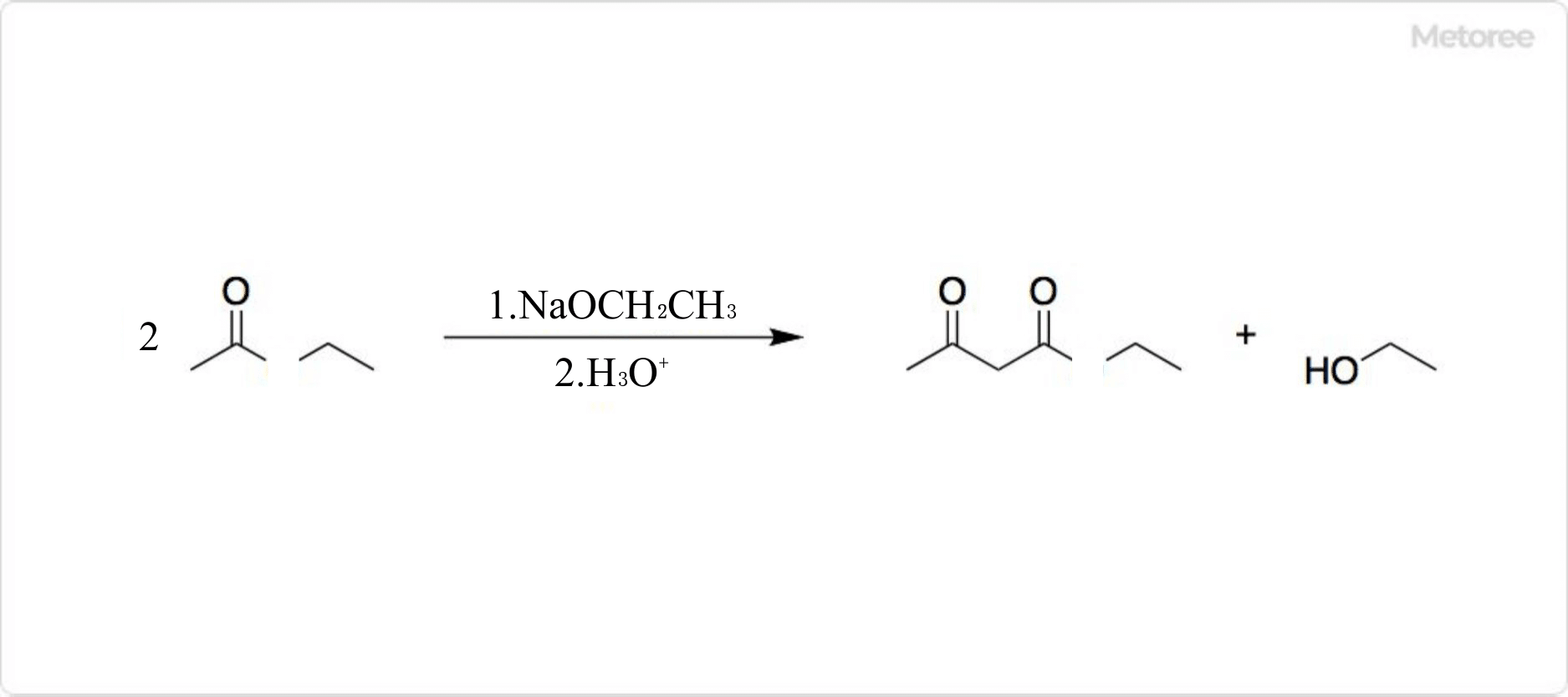
Figure 3. Synthesis of Ethyl Acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate is obtained by reacting ethyl acetate with metallic sodium or by condensation of ethyl acetate with sodium ethoxide, whose chemical formula is C2H5ONa. These reactions are known as Claisen condensation.
Industrially, ethyl acetoacetate is produced by treating diketene with ethanol.
2. Reaction of Ethyl Acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate has an active methylene moiety, forming a relatively stable carbanion with a base. An activated methylene is a methylene group adjacent to two electron-withdrawing groups, such as a carbonyl group.
Compounds with highly acidic activated methylene groups include malonate esters, cyanoacetates, and acetylacetone, offering stability for carbon-carbon bond formation. Examples include acetoacetic ester synthesis and malonic ester synthesis.
Active methylene compounds like ethyl acetoacetate are also used in cross-coupling reactions and Michael addition reactions.