What Is Zinc Sulfate?
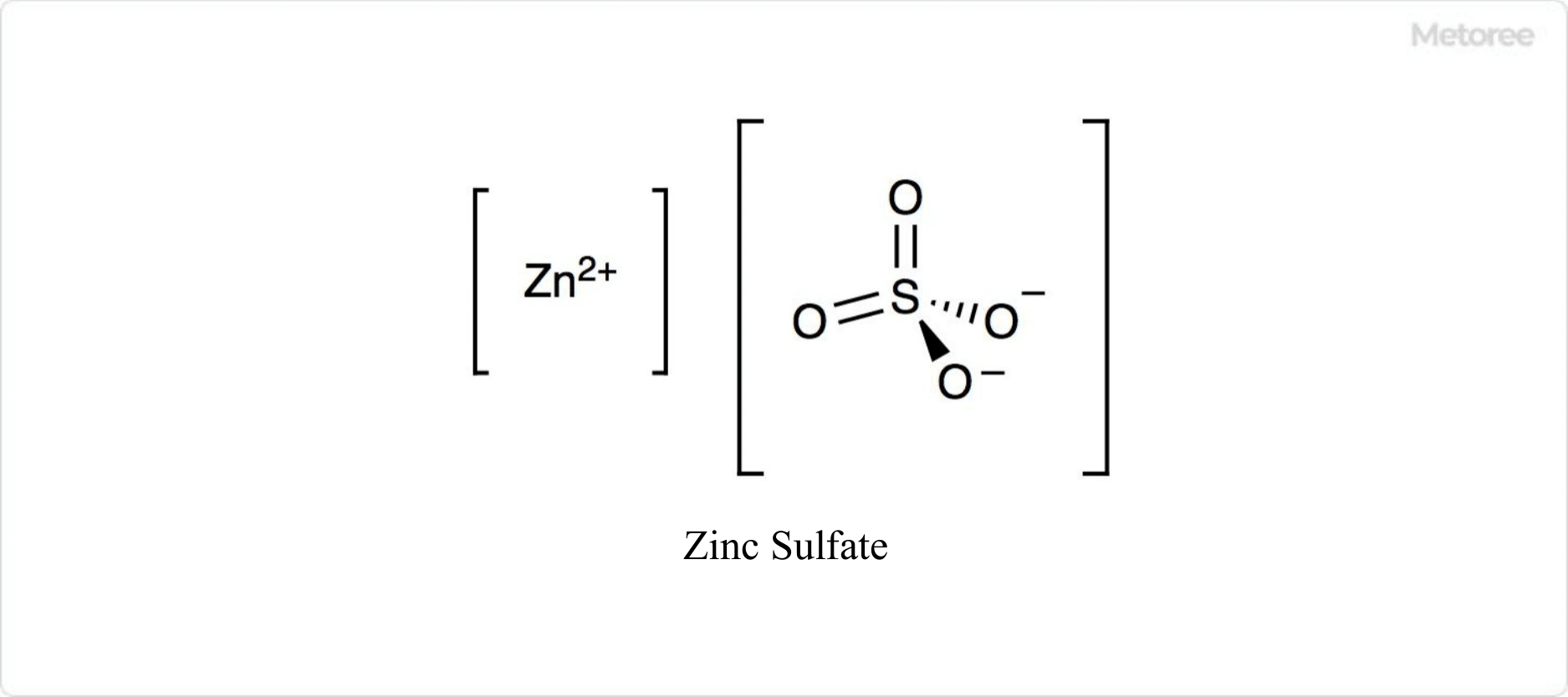
Figure 1. Structure of Zinc Sulfate
Zinc sulfate is an inorganic compound formed by the reaction of zinc sulfate and zinc.
Its chemical formula is ZnSO4. When crystallized from aqueous solution, it can form 1, 6, or 7 hydrates, depending on temperature.
Zinc sulfate powder is irritating to the eyes and is designated as a deleterious substance under the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law, and heating may produce toxic fumes and vapors. Mixing or contact with alkaline substances should be avoided in the case of zinc sulfate solutions.
Uses of Zinc Sulfate
Zinc sulfate is widely used as one of the raw materials for pharmaceutical, agricultural, and industrial products.
In pharmaceuticals, the astringent and antiseptic properties of zinc sulfate are used to make eye drops for the treatment of conjunctivitis and blepharitis. For industrial use, it is used to coagulate liquid rayon in the rayon manufacturing process and is also available as a wood preservative and paper bleaching agent. In agriculture, it is added to feed to strengthen the mineral content and mixed into Bordeaux solution, an agricultural fungicide, to prevent damage to crops.
Zinc sulfate can also be used as a food additive under certain conditions. It is added to animal feed as an essential zinc source, containing up to several hundred mg per kilogram of feed. It is considered safe in trace amounts. However, an overdose of 2-8 mg per kg of body weight can cause stomach discomfort with nausea and vomiting.
Properties of Zinc Sulfate
Zinc sulfate monohydrate is a colorless powder with a specific gravity of 3.28 at 15°C. Zinc hexahydrate is a colorless monoclinic crystal with a specific gravity of 2.072 at 15°C. Dihydrate and tetrahydrate are also known.
The heptahydrate is a colorless, odorless crystal with astringent properties. It air-dissolves in air and dissolves in crystalline water at about 50°C when heated rapidly. On gentle heating, it becomes hexahydrate at 39°C, monohydrate at 70°C, and anhydrate at 240-280°C. Heptahydrate is soluble in water and virtually insoluble in ethanol. Aqueous solutions are weakly acidic due to hydrolysis.
The anhydrate of zinc sulfate decomposes to Zn3O(SO4)2 at 600°C and to zinc oxide (ZnO) at 930°C.
Structure of Zinc Sulfate
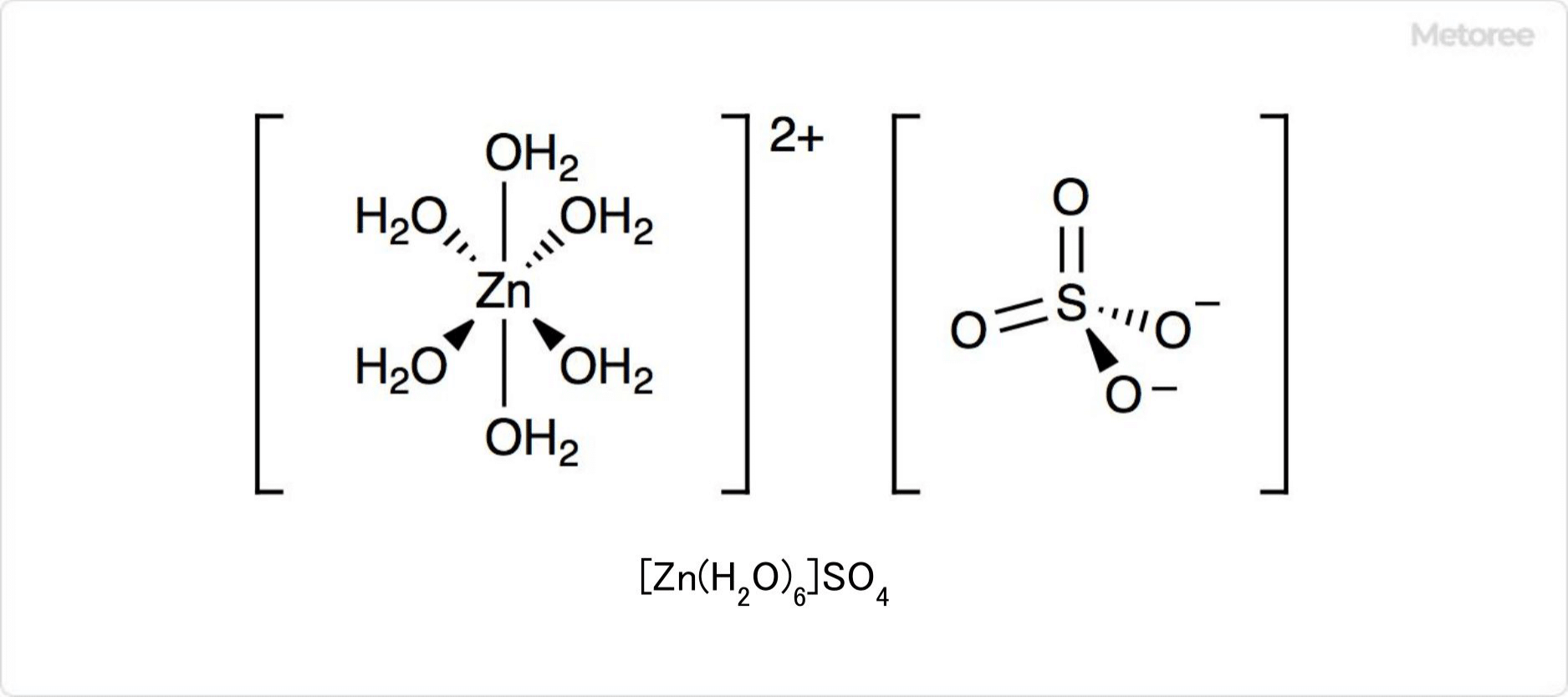
Figure 2. Zinc Sulfate in Aqueous Solution
Zinc sulfate is formed when zinc-containing materials are treated with zinc sulfate. Pharmaceutical-grade zinc sulfate can be synthesized by treating high-purity zinc oxide with zinc sulfate.
In an aqueous solution, the hydrate of zinc sulfate is composed entirely of [Zn(H2O)6]2+ and SO42-. This coordination compound has only water as a ligand and contains zinc ions. When this solution is treated with a solution containing barium ions, barium sulfate is formed.
Other Information About Zinc Sulfate
1. Natural Zinc Sulfate
ZnSO4・7H2O occurs as the mineral goslarite. (Zn, Cu, Fe)SO4-7H2O is found as a trace mineral in zinc melanterite. Low hydrates of zinc sulfate such as (Zn, Fe)SO4・6H2O (Bianchiite), (Zn, Mg)SO4・4H2O (Boyleite), and (Zn, Mn)SO4・H2O (Gunningite) are not commonly found in nature.
2. Related Compounds of Zinc Sulfate
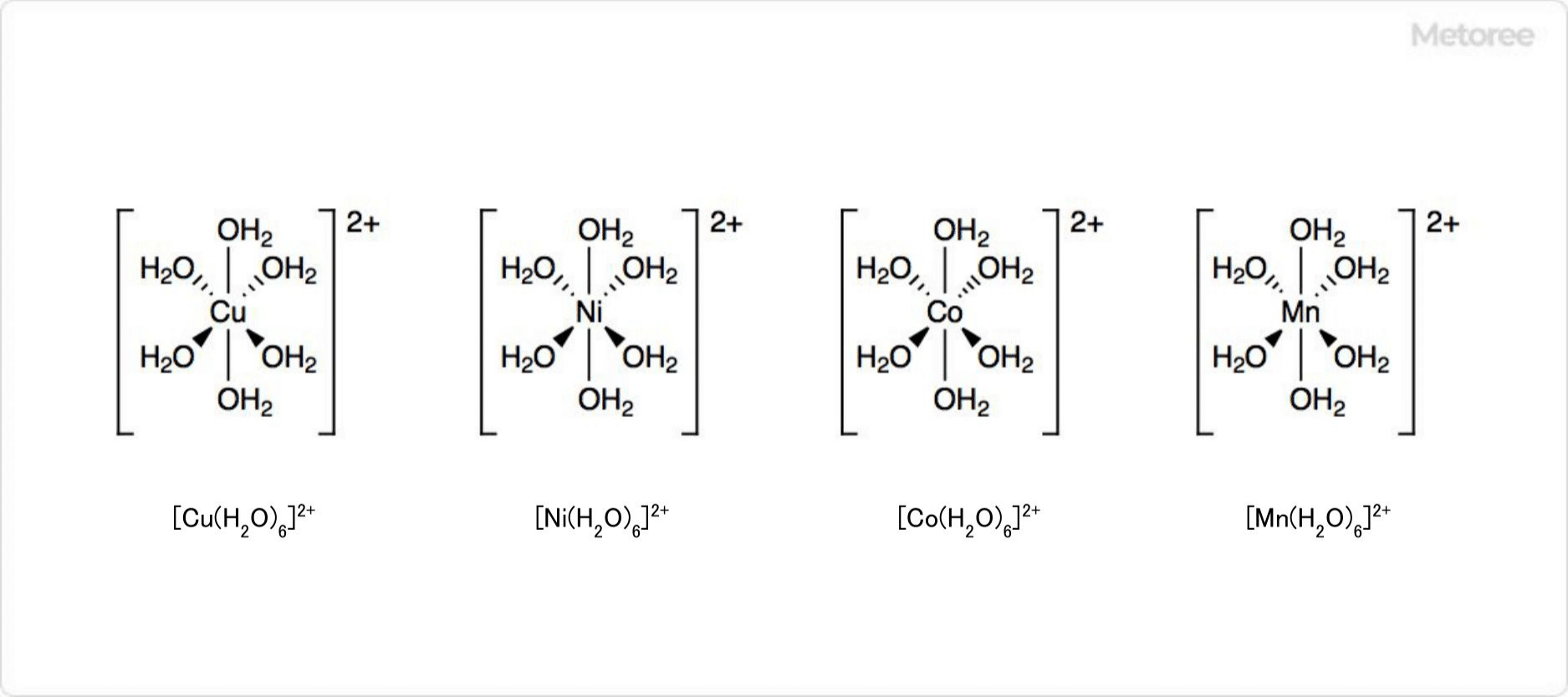
Figure 3. Related Compounds of Zinc Sulfate
Zinc sulfate 7-hydrate is orthorhombic and has the same structure as ferrous sulfate 7-hydrate and Magnesium Sulfate 7-hydrate. a = 11.779Å, b = 12.050Å, c = 6.822Å. 6 H2O molecules are coordinated to Zinc Sulfate, and 1 H2O molecules are coordinated to the oxygen of the sulfate ion.
Most metal aqua complexes are mononuclear. The general formula is [M(H2O)6]n+ (n = 2, 3), forming an octahedral structure. Examples are [Cu(H2O)6]2+、 [Ni(H2O)6]2+、 [Co(H2O)6]2+、 [Mn(H2O)6]2+. Water molecules function as Lewis bases, donating electron pairs to metal ions.