What Is an Electric Welder?
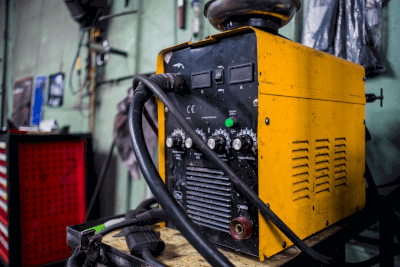
An electric welder is a tool that employs arc discharge to fuse metals together. This category includes DC inverter welders and AC arc welders. Notably, some electric welders are battery-powered, offering portability for use in areas without a power source.
Electric welders designed for standard 100 V household use are also available. Unlike processes that use flammable gases, such as acetylene, electric welders do not require special qualifications, simplifying their use.
Uses of Electric Welders
While welding machines are commonly found in metalworking factories, they are less frequent in everyday settings. However, they are invaluable for projects involving metal, such as shelf construction or crafting small metal items.
Without a welder, metal parts must be connected using screws and nuts. This method is feasible for simple shapes like pipes and plates, but more complex configurations often necessitate welding.
Principle of Electric Welders
Electric welders function by melting welding rods through arc discharges, producing temperatures high enough to liquefy metal. The molten electrode material serves as a binder, creating a robust metallic bond between the metal parts.
Typically, electric welders can join various ferrous materials, including soft iron, stainless steel, and cast iron. It is important to note that arc discharges emit intense light and harmful ultraviolet rays, necessitating eye protection during use to prevent damage.
Moreover, as electric welders involve an electric circuit, grounding the welding object is essential to avoid electric shocks.
Semi-automatic Welding Machines
Semi-automatic welders join materials by melting metal automatically supplied to a heating device or torch. These machines are categorized into gas-shielded arc welding and non-gas welding methods.
Gas-shielded arc welding involves using inert gas to protect the hot metal from oxidation. There are three types based on the shielding gas used: CO2 welding, MAG welding, and MIG welding.
CO2 welding, employing solely carbon dioxide gas, is prevalent for steel welding. MAG welding uses a mix of gases, typically 80% argon and 20% CO2, suitable for iron and stainless steel welding. MIG welding, ideal for stainless steel and aluminum, utilizes argon or an argon-oxygen mix, resulting in a clean finish but at higher operational costs.
Qualifications for Electric Welders
Using electric welders carries risks like electric shock, explosions, and fires. To mitigate these risks, specific training for electric welding workers is mandated, along with adherence to local standards and regulations. Such training covers arc welding techniques and relevant legal provisions.