What Is a Metal Film Resistor?
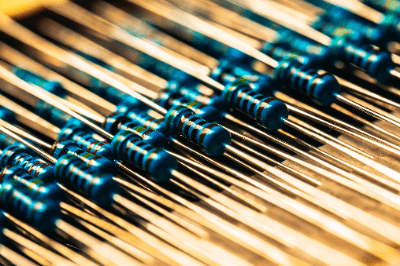 A metal film resistor is a fixed resistor that uses metal as its resistive element.
A metal film resistor is a fixed resistor that uses metal as its resistive element.
Two types of fixed resistors are widely used in general: carbon resistors and metal film resistors.
Carbon resistors use carbon as the resistive element, while metal film resistors use metal as the resistive element. They have higher resistance accuracy than carbon resistors, but are more expensive.
Uses of Metal Film Resistors
Metal film resistors are fixed resistors that use a metal film as the resistive element. They have low resistance tolerance and temperature coefficient of resistance and are highly accurate and stable resistors. They also have the advantage of suppressing current noise.
Taking advantage of these characteristics, they are widely used in equipment that handles minute signals. The following are examples of metal film resistors.
- Communication and measurement equipment in the industrial field
- Computers and peripheral equipment
- Audio-visual equipment
Carbon resistors are used for current limiting resistors such as light emitting devices and bias resistors of amplifiers, since they do not require high resistance accuracy. On the other hand, metal film resistors are used in DC amplification circuits where temperature drift is a problem, and in filter circuits where strict cutoff frequency is required.
Principle of Metal Film Resistor
The resistive element of a metal film resistor is mainly composed of metal. Nickel-chromium is generally used as the material. Compared to carbon resistors, metal film resistors have advantages such as higher accuracy, but are more expensive.
There are two types of metal film resistors: thick film type and thin film type. Thin-film type is a higher precision (±0.05%) version of thick-film type.
Thick-film type is made by heating and firing metallic paste, while thin-film type is made by vapor-depositing or coating metal. While the temperature characteristics of metals in general are positive, the temperature coefficient of metal film resistors is reduced by changing the alloy ratio. Therefore, the ratio determines whether the resistor will have a positive or negative characteristic.
How to Select Metal Film Resistors
Metal film resistors are selected based on their resistance value. Resistors are available in two types: those with resistance printed on them and those with color-coded resistors.
In the case of color code indication, the “upper two digits” or “upper three digits” of the resistance value are indicated in 10 colors, with black as 0 and gray as 9. By reading this, the resistance value of the resistive element can be ascertained. Similarly, multipliers, tolerances, temperature coefficients, etc. can also be determined by the color code system.
Resistance tolerances are generally ±5% for carbon resistors, and ±2%, ±1%, and ±0.5% for metal film resistors, allowing the selection of products with minimal errors. Carbon resistors show a negative temperature series of -200 to -800ppm/°C. Metal film resistors show a negative temperature series of -200 to -800ppm/°C. Metal film resistors have relatively small temperature variation and can be selected from ±200ppm/℃, ±100ppm/℃, and ±50ppm/℃.
Other Information on Metal Film Resistors
Color Display of Metal Film Resistors
Lead wire type or MELF type resistors indicate resistance value, error, and temperature coefficient by color code.
There are four types of bands indicated on the resistors, from three to six bands, but four and five bands are commonly used. The two or three bands from the left represent the resistance value, and the one band after that represents the multiplier.
Carbon resistors usually have a 4-band display. The fourth band indicates the error, which is generally gold (5%).
Metal film resistors, on the other hand, have three significant digits due to their high accuracy. The fifth digit indicates the error, but green (0.5%), brown (1%), and red (2%) are also used.