What Is a Photodiode?
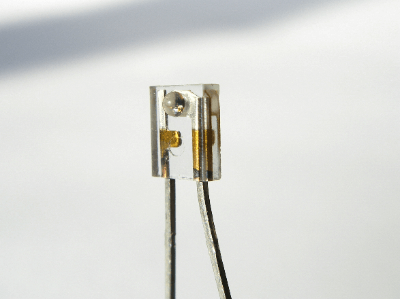
A photodiode is an electronic component in which a minute electric current flows in a fixed direction when irradiated by light.
When a semiconductor is irradiated with light, the photoelectric effect causes electrons to be emitted by the excited atoms, creating an electric current. This mechanism is used to detect light.
Because of their high accuracy, photodiodes are especially necessary for optical communication devices. Photodiodes are also incorporated in other medical devices such as gas concentration measurement.
There are mainly PN junction, PIN junction, and avalanche types, each with different light-receiving sensitivities and response speeds, and they are used in different ways.
Uses of Photodiodes
Components with similar characteristics to photodiodes include photoresistors and CCDs.
PN-junction photodiodes are used in CD players, TV remote controls, and video tape recorders.
When a large number of PN-junction photodiodes are grouped and used side by side, they become solar cells.
On the other hand, PIN junction photodiodes are more sensitive than PN junction photodiodes and are used in optical communication systems that require more accurate detection.
They are also used in medical equipment such as tomographic X-ray machines.
Principle of Photodiodes
When light is irradiated onto a photodiode, the atoms in the semiconductor junction are excited, releasing electrons, which form an electric current; this way light can be detected by measuring the current.
The wavelength of light that can be detected depends on the material of the diode, so this must be selected according to the application. Major materials include silicon, germanium, and lead sulfide.
1. PN Junction Type
When light is irradiated to the depletion layer at the boundary between P-type and N-type semiconductors, electrons flow toward the N-type semiconductor, and holes are formed in the P-type semiconductor due to the electron transfer.
Since a flow of electrons occurs while light is irradiated, the diode operates by detecting the flow of electrons. The downside is that the response speed is somewhat slow.
2. PIN Junction Type
This is the most widely used type of photodiode due to its low noise.
A P-type semiconductor, an I-type semiconductor, and an N-type semiconductor are functioned in a sequence. By applying a reverse bias voltage to the I-type semiconductor, excited electrons can flow smoothly to the N-type semiconductor, resulting in a faster response speed.