What Is a Proximity Switch?
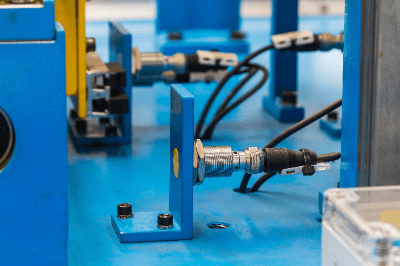
A proximity switch is a non-contact switch that can detect the proximity of a metallic object.
It detects the proximity of a metallic object using electromagnetic induction, etc., and outputs as a contact point. There are various lineups of power supply requirements and contact configurations required for proximity switches, and they must be selected according to the situation.
Uses of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches are used in factories and other equipment to detect the drive status of machines. Specific uses of proximity switches are as follows:
- Detection of hydraulic press operation
- Motion detection for industrial robots
- Open/close status detection of critical valves and doors
- For servomotor positioning detection
- Rotation speed detection of rotating equipment
Machine operation is detected at the above locations and alarms are issued or sequence control is implemented. In recent years, waterproof and heat-resistant products are also available. Since the machine status can be easily detected by attaching a piece of iron, etc., they are often used for large equipment in the iron and steel industry.
Principle of Proximity Switches
There are various types of proximity switches, but inductive proximity switches are the most commonly used. Inductive proximity switches consist of an electromagnetic coil, an oscillator circuit, and a casing.
1. Electromagnetic Coil
An electromagnetic coil is a component that generates an induced current in an approaching metal. The electromagnetic coil always outputs a high-frequency magnetic field, and electromagnetic induction is generated when a metal object such as a piece of iron comes close to it. This electromagnetic induction generates an induced current in the metallic object.
2. Oscillation Circuit
The oscillation circuit is a component that feeds back the power output by the electromagnetic coil. The induced current generated inside a metallic object is converted to heat within the metal, resulting in a power loss. The oscillation circuit detects this power loss and sends it to the output circuit. The transmitter circuit and output circuit are configured on the same board, and the output circuit outputs the power as a contact signal to the outside.
3. Casing
The casing is the outer frame that protects these circuit components. The casing is often threaded and secured to the mechanical device with a locknut. The casing is usually filled with resin to insulate the casing from the circuit components.
Other Information on Proximity Switches
1. Positioning of Proximity Switch
When using proximity switches, the mounting position must be determined. Proximity switches are non-contacting and output a contact point when they detect the proximity of a metal or other contact object. Positioning of proximity switches means adjusting the proximity distance to the object to be contacted by adjusting the position of the proximity switch.
Proximity switches have a fixed detection distance according to their specifications. The proximity switch output operates when the object to be detected enters this detection range. If the proximity switch is too far away, it will not operate, so it is necessary to determine the proper distance by adjusting the position of the proximity switch.
Products are also available that indicate the response of the proximity switch by emitting LED light. Such products are convenient for positioning because the output operation can be visually observed at close range. It should be noted, however, that the LED emission pattern differs depending on the product. Some products emit light even in locations that are within the detection range but not yet in the output operation range. Such products often emit multiple colors.
For example, there are products that emit orange when the detected object is in the detection range and green when the detected object is brought even closer to the proximity switch for output operation. Therefore, it is important to read the instruction manual of the product to be used carefully .
2. Failure of Proximity Switch
When a proximity switch malfunctions, a failure of the proximity switch is suspected. There are many possible reasons for the failure, but the two most common causes are as follows:
Power Failure
Check that the power supply to the proximity switch is correct using a tester or similar device. If there is no power supply, the cause is the loss of power. If the power circuit or grounding is not correct, there will be no signal output even if the object is to be detected approaches. In this case, disconnection of the power circuit or ground wire or failure of the power supply unit is suspected.
Misalignment of Proximity Switch
Misalignment of the mounting position may also be a cause. If misalignment causes the switch to move away from the detection range, it can be restored by adjusting the position. However, if the object to be detected comes too close and contacts the proximity switch, the proximity switch may be damaged physically .
If physical damage is the cause, the proximity switch must be replaced. Other possible causes of proximity switch failure include noise and overvoltage.
3. Proximity Switch and Detectable Object
Proximity switches are mainly used to detect metallic objects. The reason is that they use electromagnetic induction as their operating principle. In order to generate electromagnetic induction, the piece of iron to be detected must be conductive.
However, in recent years, inductive proximity switches have been developed that can sensitively detect even metals that are not conductive.