What Is Methylcyclohexane?
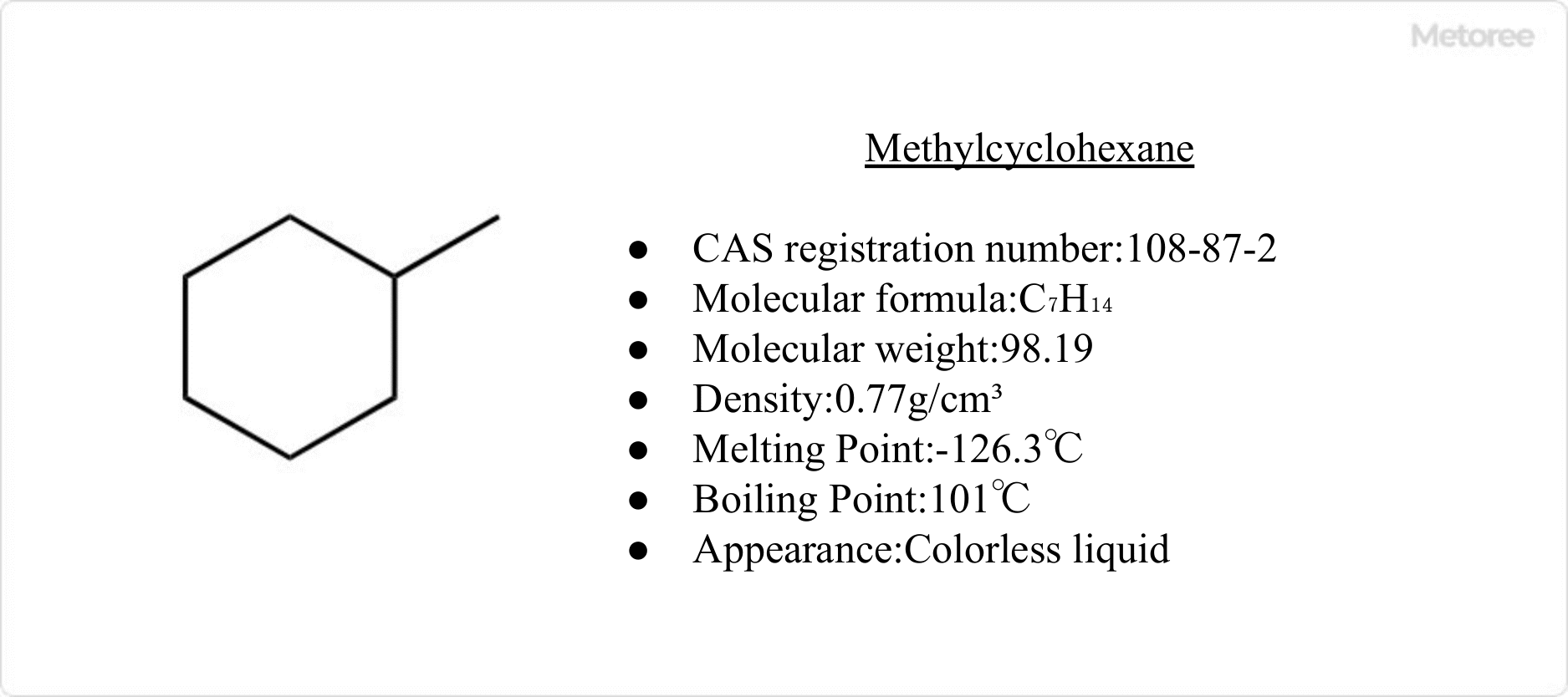
Figure 1. Basic information on methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane is a clear, colorless or nearly colorless liquid organic compound with a characteristic odor.
Uses of Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane is a type of distillate obtained from heavy oil. It is used as a solvent in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as in correction fluid and jet fuel. For example, JP-7 (Jet Propellant 7), a jet fuel developed by the US Air Force for supersonic aircraft, contains about 20-30% methylcyclohexane.
In the automotive industry, methylcyclohexane is being explored as a potential fuel for hydrogen-powered fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), and it has recently gained attention as a household name.
Methylcyclohexane can be converted to hydrogen for transportation and storage, allowing hydrogen to be stored as a liquid compressed to 1/500 of its volume. Therefore, methylcyclohexane may play a significant role in the future of FCVs as the shift to electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly increasing as a way to combat global warming.
Properties of Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane has the chemical formula C7H14, molecular weight 98.19, melting point -126°C, and boiling point 100°C. It is extremely soluble in acetone and virtually insoluble in water. Methylcyclohexane is sometimes abbreviated as MCH.
Its CAS number is 108-87-2.
Structure of Methylcyclohexane
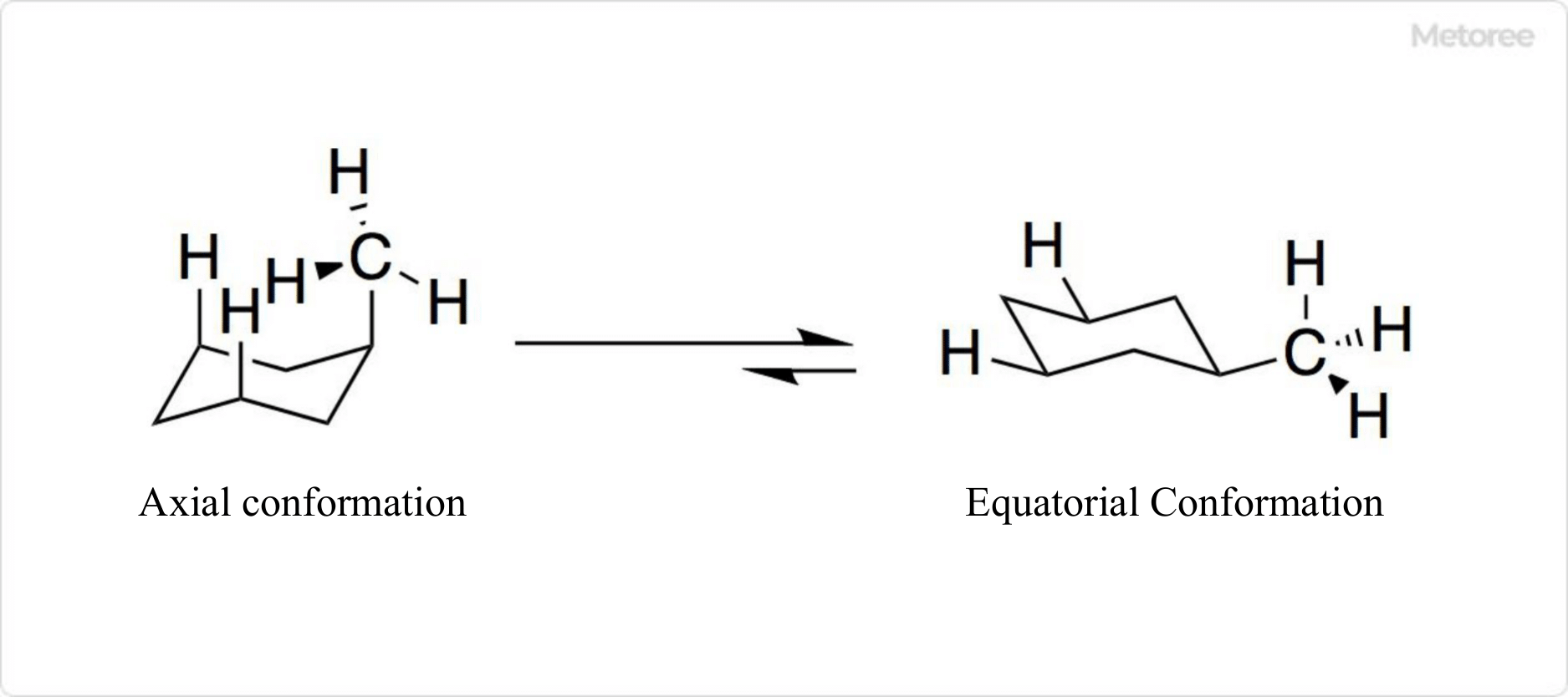
Figure 2. Structure of methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane is a cycloalkane with one methyl group attached to a cyclohexane ring. It typically adopts a chair-shaped conformation.
In methylcyclohexane, the hydrogen atoms of the methyl group at position 1 and those at positions 3 and 5 experience steric hindrance. Therefore, the equatorial conformation is generally more stable than the axial conformation, due to 1,3-diaxial interactions.
Other Information on Methylcyclohexane
1. Hydrogen Storage With Methylcyclohexane
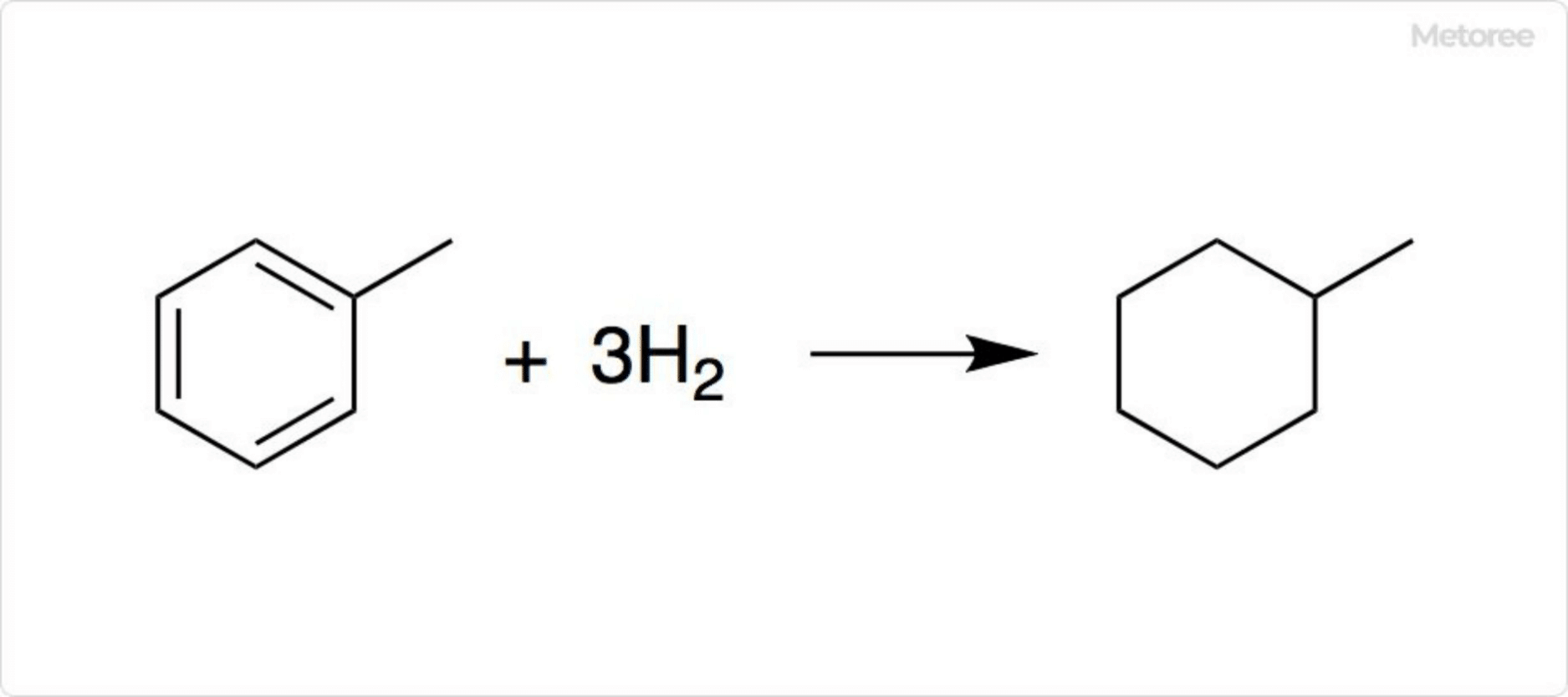
Figure 3. Mechanism of hydrogen storage in methylcyclohexane
Hydrogenation of toluene produces methylcyclohexane. Hydrogen can be extracted by dehydrogenation using a catalyst. As an organic hydride, methylcyclohexane is being studied as a stable method for hydrogen storage and transportation.
The theoretical hydrogen storage density of methylcyclohexane is 47.0 kg-H2/m3. The storage density is somewhat lower than that of benzene and cyclohexane (56.0 kg-H2/m3) and naphthalene and decalin (65.4 kg-H2/m3). However, methylcyclohexane has the advantage of maintaining a liquid state over a wide temperature range.
2. Applications of Methylcyclohexane
Several companies have developed dehydrogenation catalysts for methylcyclohexane and have successfully demonstrated hydrogen supply on a commercial basis. Another company has received an order for a hydrogen generation system combining methylcyclohexane and wind turbines at Showa Station in Antarctica.
3. Safety of Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane has low photochemical reactivity, making it less likely to contribute to photochemical smog. It is less toxic than xylene and toluene.