What Is Alloy Tool Steel?
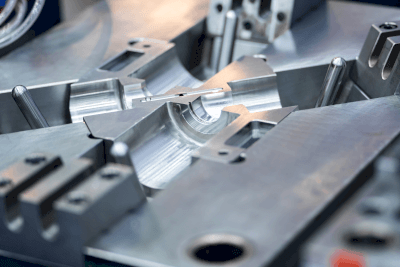
Alloy Tool Steel is a steel material generally characterized by high hardness, wear resistance, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and strength.
It is used in the manufacture of tools and machine parts, and its properties are generally improved by adding various metallic elements (chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, etc.) to carbon tool steel.
Alloy Tool Steel can be heat treated to adjust its hardness and strength. It is usually heated to high temperatures and cooled rapidly in a process called quenching, which increases hardness and at the same time makes them brittle, so moderate forging, machining, and heat treatment are necessary to control the hardness.
Uses of Alloy Tool Steel
1. Cutting Tools
Alloy Tool Steels such as high speed steel (HSS), and molybdenum steel are used.
2. Dies
Tool steel and tungsten steel are used for dies. Examples include molds for plastic molding and molds for casting.
3. Machine Tools
Alloy Tool Steel such as high speed steel and molybdenum steel are used for machine tools. Machine tool blades, machine tool drive parts, and bearings are examples.
4. Automotive Parts
Alloy Tool Steel, such as high-speed steel and chrome vanadium steel, is used for automotive parts. Examples include engine valves, chassis, and gears.
5. Aircraft Parts
Alloy Tool Steels such as high speed steel, tungsten steel, and molybdenum steel are used for aircraft parts. Examples include jet engine parts, fuel system pipes, and control system parts.
6. Other
Alloy Tool Steels such as high speed steel and chrome vanadium steel are used in a variety of industries. Examples include construction materials, precision machinery, electronics, and sporting goods.
Types of Alloy Tool Steel
1. For Cutting Tool Steel
Alloy Tool Steel for cutting tools are characterized by high hardness and heat hardenability, and can be used for high-speed cutting. They are highly durable and can withstand prolonged use.
2. For Impact Resistant Tool Steels
Alloy Tool Steel for impact resistant tool steels have higher impact resistance than carbon steel, and is less likely to be deformed or broken even when subjected to blows or vibrations.
3. For Cold Working Dies
Alloy Tool Steel for cold dies are suitable for molds used at room temperature.
4. For Hot Work Molds
Alloy Tool Steel for hot work tooling have properties suitable for molds used at high temperatures.
How to Select Alloy Tool Steel
The main factors to consider when selecting alloy tool steel are as follows:
1. Cutting Conditions
The required hardness and wear resistance vary depending on the cutting conditions, such as cutting speed, feed rate, machining depth, cooling method, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to check the cutting conditions and select an appropriate alloy tool steel.
2. Required Performance
Alloy Tool Steel has various performances such as hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance, machinability, and heat treatment performance. Depending on the required performance, the appropriate alloy tool steel should be selected.
3. Material Shape and Size
Depending on the shape and size of the alloy tool steel material, its machining and heat treatment performance will vary. For example, alloy tool steel with a finer grain size is suitable for small blades and tools.
4. Cost
Procurement cost should also be considered when selecting an appropriate alloy tool steel. High quality alloy tool steel can be expensive.
Properties of Alloy Tool Steel
Specifically, alloy tool steel has the following properties:
- High hardness
Harder than carbon steel, making it suitable for applications such as cutting and imitation machining. - Wear resistance
Resistant to abrasion and friction, performance is maintained even after long-term use. - Heat resistance
Suitable for high-temperature processing as it does not deform or soften even when used at high temperatures. - Corrosion Resistance
Highly resistant to corrosion and damage caused by corrosion. - Fatigue resistance
High strength under repetitive loading provides excellent durability, as it does not fail under fatigue even after long-term use.
Other Information on Alloy Tool Steel
General Alloying Elements
Common alloying elements and their effects are described below. The alloying elements listed below affect the properties of the steel depending on the proportion added to the steel and other addition conditions. The amount of alloying elements added has a significant effect on the properties of the steel, and therefore the optimum amount should be established.
1. Chromium (Cr)
Chromium is added to improve corrosion resistance. By forming oxides and protecting the surface, it also improves resistance to corrosion, as well as the hardness and strength of the steel.
2. Vanadium (V)
Vanadium is added to increase strength. It is characterized by the formation of fine particles that strengthen the crystalline structure of the steel, thereby increasing its strength. It is also used to improve wear resistance.
3. Molybdenum (Mo)
Molybdenum is added to steels to make them suitable for use at high temperatures. It improves resistance to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures and also increases the strength and hardness of the steel.
4. Manganese (Mn)
Manganese is an alloying element added to increase hardness and strength. It also oxidizes the surface of steel during heat treatment and promotes surface hardening.
5. Nickel (Ni)
Nickel is added to improve corrosion resistance. Like chromium, it improves resistance to corrosion by forming oxides and protecting the surface. It also contributes to the strength of steel through heat treatment.
6. Cobalt (Co)
Cobalt is added to steels to make them suitable for use at high temperatures. It improves resistance to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures and also increases the hardness and strength of the steel.
Various other alloying elements are also used, such as tungsten (W), which improves hardness, strength, and machinability. Silicon (Si) is used to increase strength and control deformation during heat treatment.
Combinations of alloying elements produce alloy tool steels with a variety of properties. For example, alloy tool steel combining chromium and vanadium can improve both corrosion resistance and strength. Alloy tool steel combining chromium and nickel is also suitable for use at high temperatures.