What Is an MPU?
 An MPU, or Micro Processing Unit, is a semiconductor device crucial in computing and logical processing. Commonly known as a microprocessor, it occupies a central role in computers and other digital devices. With advancements in semiconductor technology, modern MPUs feature billions of transistors on a single chip, enabling more compact and energy-efficient devices.
An MPU, or Micro Processing Unit, is a semiconductor device crucial in computing and logical processing. Commonly known as a microprocessor, it occupies a central role in computers and other digital devices. With advancements in semiconductor technology, modern MPUs feature billions of transistors on a single chip, enabling more compact and energy-efficient devices.
Applications of MPUs
MPUs are integral to all computers, managing operations in conjunction with memory, storage, and input/output devices. They are also used alongside GPUs for graphics processing and vector processors for AI processing in applications like 3DCG and recognition tasks. While MPUs serve general-purpose computing, MCUs are deployed in specialized areas like home appliances, industrial equipment, and automotive control systems.
Principles of MPUs
MPUs house a CPU that processes instructions and data from memory. They feature a memory management unit for address translation and built-in cache memory for faster access and processing. The MPU’s operation is governed by a clock signal from a clock generator, with some models operating at several GHz, enabling rapid computational capabilities.
Types of MPUs
MPUs are classified into CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) based on their architectural design. CISC MPUs execute complex processes with fewer instructions, while RISC MPUs, with their fixed-length instruction set, are tailored for high-speed execution in general computing applications. Additionally, VLIW (Very Long Instruction Word) MPUs are known for handling multiple instructions simultaneously at high speeds.
Evolution of MPUs
MPU technology has evolved from the early 4-bit Intel 4040 to the latest multi-billion transistor models operating on nanometer-scale process rules. As semiconductor technology continues to advance, developments in vertical transistor formation and explorations into optical semiconductors and quantum processors are shaping the future of MPU technology.
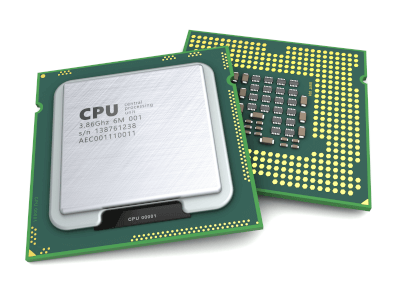 The Central Processing Unit (
The Central Processing Unit (
 A box cutter is a versatile
A box cutter is a versatile  A ratchet handle is part of a
A ratchet handle is part of a  A porcelain tile drill bit is a specialized drilling accessory designed for use with electric drills, a common power tool. These bits are compatible with standard models of power tools, including some multi-impact drivers with flat impact adjustment settings.
A porcelain tile drill bit is a specialized drilling accessory designed for use with electric drills, a common power tool. These bits are compatible with standard models of power tools, including some multi-impact drivers with flat impact adjustment settings.
 A door stay is a device that regulates the opening and closing speed of hinged doors, such as entrance doors, storage doors, or lids.
A door stay is a device that regulates the opening and closing speed of hinged doors, such as entrance doors, storage doors, or lids. An impact screwdriver is a term broadly used for a range of electrically powered screwdrivers. It often refers to power tools, including
An impact screwdriver is a term broadly used for a range of electrically powered screwdrivers. It often refers to power tools, including  A jigsaw blade is the blade of an electric saw known as a jigsaw. The right blade is selected based on the material being cut, whether it’s wood or metal. By replacing the blade, the range of materials and shapes that can be processed is expanded. Sometimes, the jigsaw blade may need replacement due to wear and tear.
A jigsaw blade is the blade of an electric saw known as a jigsaw. The right blade is selected based on the material being cut, whether it’s wood or metal. By replacing the blade, the range of materials and shapes that can be processed is expanded. Sometimes, the jigsaw blade may need replacement due to wear and tear.