What Is a Non-contact Tachometer?
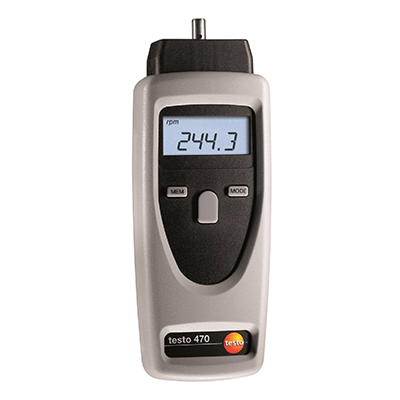

Non-contact tachometers are used to measure the rotation of rotating industrial equipment.
Rotating equipment is measured in a variety of ways, which is very important because its rotation can determine the capacity of the equipment.
However, it is time-consuming and dangerous to use a contact tachometer to measure the rotation of rotating equipment when there is no need for constant monitoring.
Non-contact tachometers are used for performance testing of rotating equipment which can be easily measured. There are various types of tachometers, from handy types to permanently installed types.
Uses of Non-contact Tachometers
The rotational speed of equipment which uses motors is very important.
For example, the performance of a roots blower can be determined from its rotation speed, allowing a performance test to be conducted before shipment to the customer. Non-contact tachometers are used to measure rotational speed. Because this type of equipment does not require constant monitoring, the non-contact type is sufficient.
However, even for instruments that require constant monitoring, the non-contact type is preferred because contact-type tachometers cannot detect accurate rotation speeds due to wear and tear caused by years of use.
Principle of Non-contact Tachometers
Non-contact tachometers come in a variety of types. The strobe type has been around for a long time.
This type of tachometer detects the number of rotations by matching the period of the light with the number of rotations. When the number of times the strobe light blinks synchronizes with the rotation speed, the object appears to stand still.
The number of rotations displayed at this time can be used to measure the number of rotations.
Other types of non-contact tachometers measure revolutions per minute (RPM) by emitting red visible light. A reflector-like object is attached to the shaft or pulley of a rotating device, and red visible light shines on it.
This allows the light to be reflected at regular intervals, making it possible to measure the number of rotations.
Non-contact tachometers can be made. To make a non-contact tachometer, combine a proximity sensor with an iron plate. Attach the iron plate to a pulley and attach the proximity sensor that reacts to the iron plate. The proximity sensor will then respond at a certain cycle, allowing the device to be used as a non-contact tachometer.
There are various types of non-contact tachometers. For most of them, it is important to know the diameter or circumference of the pulley or shaft in advance. This is because even with the same pulse, if the circumference changes, the rotation speed will also change.
 An electrolytic capacitor is a
An electrolytic capacitor is a 
 Waterproof connectors are connectors that prevent water from entering the electrical wiring and prevent electrical problems, such as shorts between terminals from occurring, even if the connector is exposed to water.
Waterproof connectors are connectors that prevent water from entering the electrical wiring and prevent electrical problems, such as shorts between terminals from occurring, even if the connector is exposed to water.