What Is Aldrin?
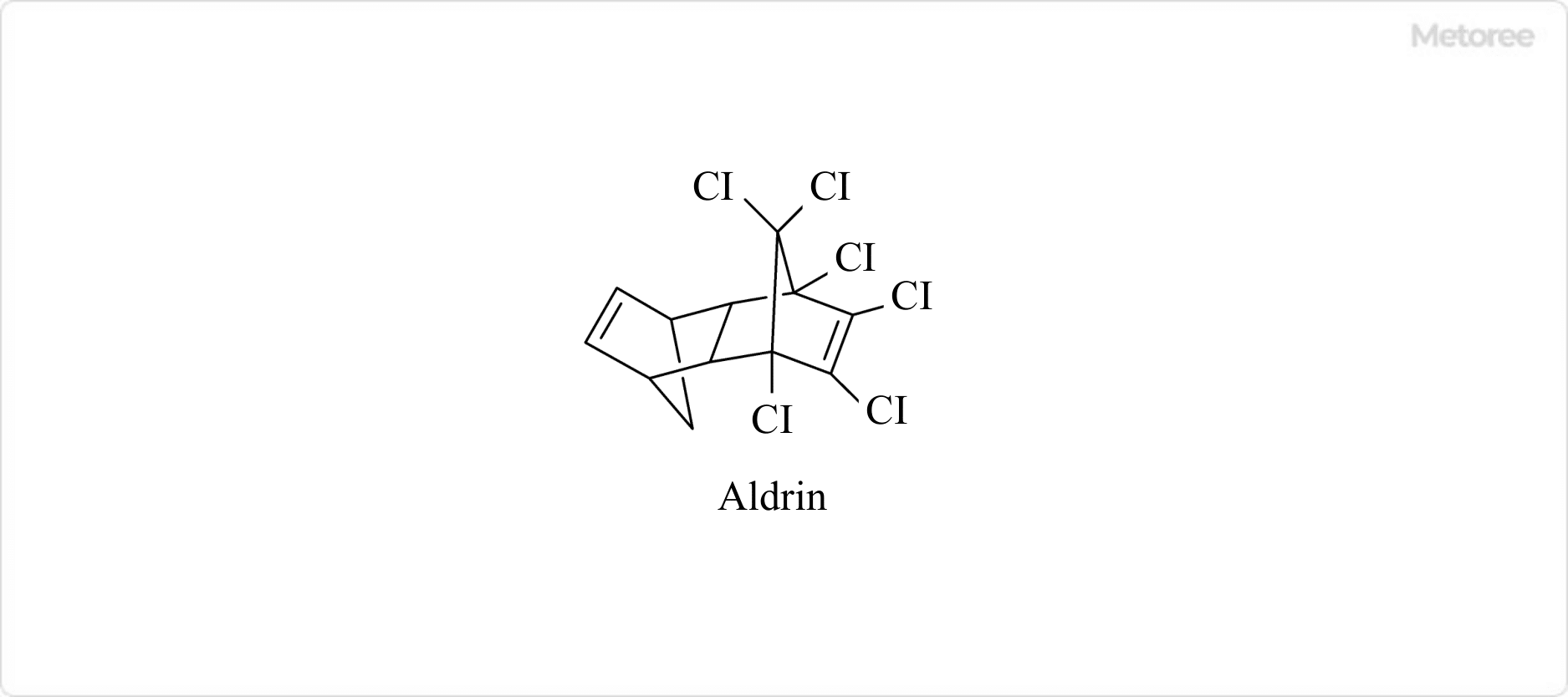
Figure 1. Structure of aldrin
Aldrin is a stable white solid organic compound with the chemical formula C12H8Cl6.
It is also known as 1,2,3,4,10,10-hexachloro-1,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-exo-1,4-endo-5,8-dimethanonaphthalene. Used as a pesticide and insecticide until the 1970s.
Aldrin is listed as deleterious and is carcinogenic, mutagenic, paraneoplastic, and teratogenic (reproductive toxicity). It is also a substance whose production and use is prohibited in principle by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.
Uses of Aldrin
Until the 1970s, Aldrin was used in large quantities in soil and seeds as a pesticide and insecticide, as well as in wood preservatives and insect-repellent paints.
However, due to Aldrin’s insolubility and extreme stability in water, it was discovered that it remained in the environment and developed toxicity over a long period.
Currently, Aldrin is mainly used as a reagent for residue testing.
Properties of Aldrin
| Chemical formula | C12H8Cl6 |
| English name | Aldrin |
| CAS No. | 309-00-2 |
| Molecular weight | 364.91 g/mol |
| Melting point/freezing point | 104-105°C |
| Boiling point or first distillation point and boiling range | 145°C (2mmHg) |
1. Aldrin Solubility
Aldrin is slightly soluble in water. It is also soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and acetone.
2. Aldrin’s Stability
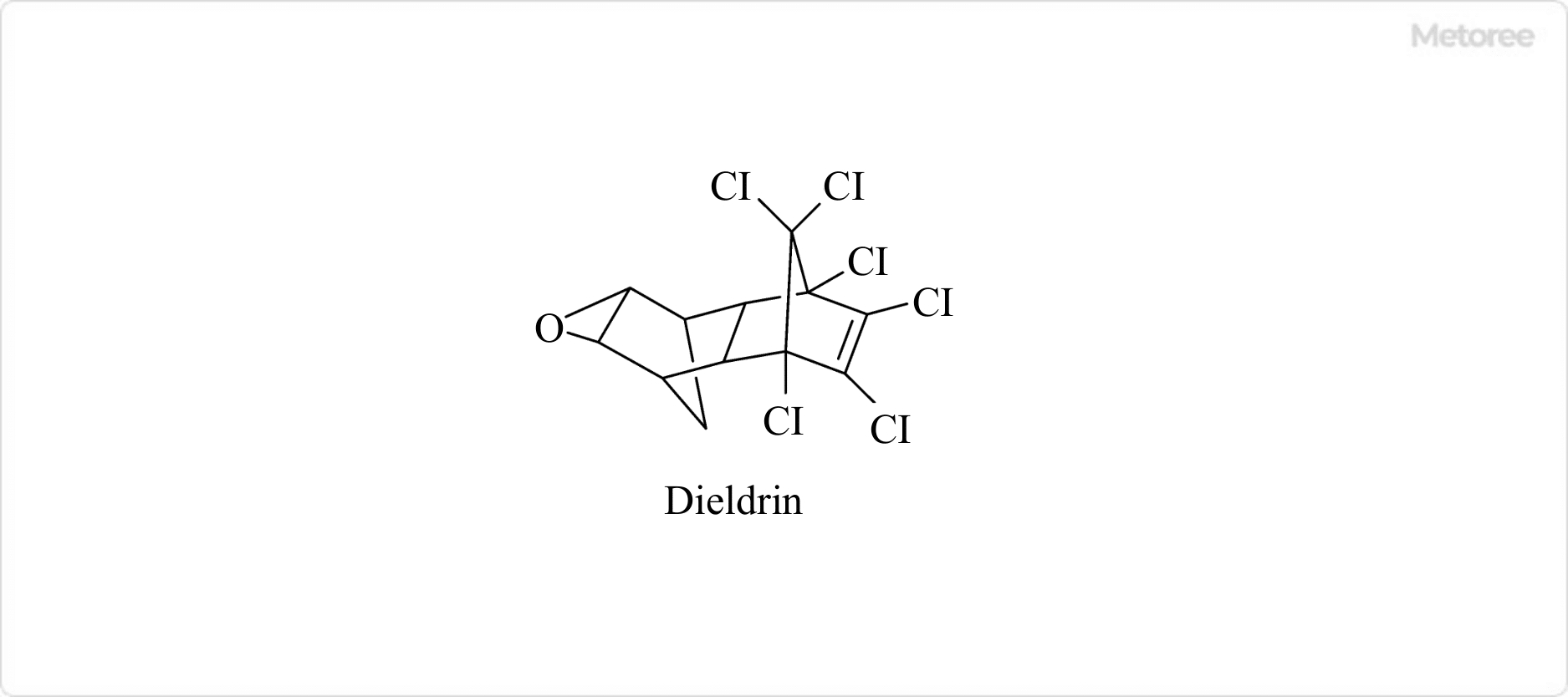
Figure 2. Structure of dieldrin
When Aldrin is applied as a pesticide in the environment, it is oxidized in soil or on plant surfaces and changes to a structure with an epoxide skeleton called dieldrin for a long period and continues to exhibit toxicity.
Therefore, both Aldrin and dieldrin are regulated as persistent organic pollutants.
Other Information on Aldrin
1. Aldrin Production Process
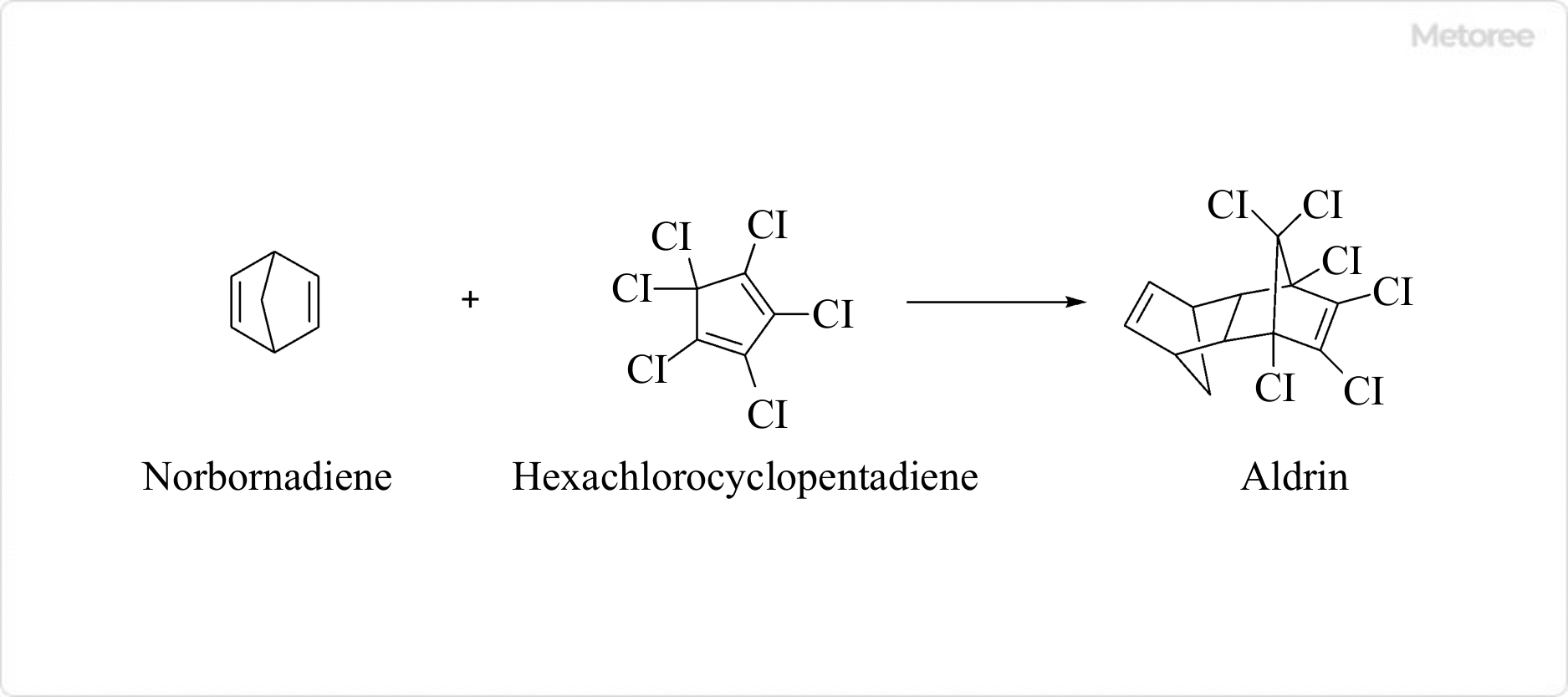
Figure 3. Method for producing Aldrin
Aldrin is synthesized by the Diels-Alder reaction using norbornadiene and hexachlorocyclopentadiene as raw materials. The Diels-Alder reaction is a versatile cycloaddition reaction, the developers of which, Otto Diels and Kurt Alder, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950.
The compound Aldrin is named after Kurt Alder.
2. Aldrin’s Toxicity
Aldrin may be life-threatening if ingested orally, dermally, or inhaled, and should be handled with extreme caution. There is no acute degradability.
3. Precautions for Aldrin Use
Because Aldrin is acutely toxic through dermal, oral, and inhalation exposure, the use of respiratory protection, protective gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing is recommended when handling Aldrin. In the unlikely event of skin contact or ingestion, immediate action is required. It is recommended that you carefully review the safety data sheet before using Aldrin.
In addition, aldrin decomposes when heated, producing toxic and corrosive gases (fumes) including hydrogen chloride. Aldrin should be stored in an appropriate storage location and away from fire.
4. Disposal method
Aldrin are compound that must not be released into the environment because of its potential impact on the surrounding environment. When disposing of Aldrin and its container, ask a professional waste disposal company licensed by the prefectural governor to dispose of it properly.