What Is a Tank Lorry?
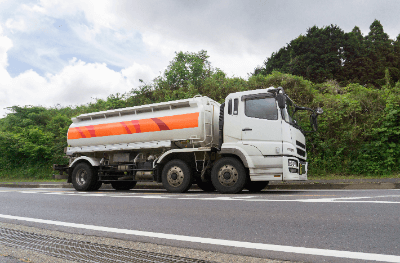
A tank lorry refers to a cargo vehicle designed to transport liquids or gases in tanks.
The term “lorry” is essentially synonymous to “truck.” The transported goods include not only hazardous materials such as petroleum and chemicals specified by fire laws but also non-hazardous items like drinking water, milk, honey, raw concrete, and high-pressure gases.
The tank’s shape, usually cylindrical and essentially elliptical, ensures structural strength. However, tanks requiring pressure containment, such as those for gases, have a circular cross-section. The tank lorry’s tank volume is determined by the nature of its contents.
According to fire regulations, hazardous materials are limited to a maximum of 30,000 liters, high-pressure gases are limited to less than 18,000 liters, toxic gases excluding ammonia are limited to less than 8,000 liters, and non-hazardous materials do not have specific regulations.
Uses of Tank Lorries
Tank lorries are categorized based on their usage, such as powder and granule transport lorries, hazardous material lorries, and high-pressure gas tank lorries.
1. Powder and Granule Transport Lorries
Powder and granule transport lorries are used to transport powdered or granulated materials such as flour, sugar, feed, sand, and cement. If the transported materials are non-hazardous, and the driver holds the appropriate driving license based on the vehicle type and size, transportation operations can be conducted.
2. Hazardous Material Lorries
Hazardous material lorries are utilized for transporting materials classified as hazardous, such as petroleum, as defined by fire regulations. In addition to the appropriate driving license based on the vehicle type and size, a person with hazardous materials handling qualifications must accompany the driver. Transportation is also possible if the accompanying person, not the driver, holds hazardous materials handling qualifications.
3. High-Pressure Gas Tank Lorries
High-pressure gas tank lorries are employed for transporting compressed gases and liquefied natural gases, as stipulated by the High-Pressure Gas Safety Act.
Principles of Tank Lorries
The loading and unloading of tank lorries vary based on the nature of the cargo. Gases, for instance, are pressurized using a compressor and filled and discharged through pressure differentials. Pumps can be used for discharge and suction.
For liquids like petroleum, the lower part of the tank is pressurized from the facility side through piping to fill the tank under pressure, and gravity is used for discharge. In the case of common liquids, loading and unloading are possible by opening the top lid of the tank and discharging from the bottom outlet. Pumping may also be used for discharge.
Structure of Tank Lorries
1. External Structure
A manhole, with an injection port, is installed on top of the tank. When transporting hazardous materials, fire regulations mandate the installation of protective frames near the manhole.
At the bottom, there is a valve for discharging the load, which can be opened and closed using a handle. An air safety valve for pressure adjustment is installed externally to the tank. There are also measuring devices for calculating the amount of the load.
2. Internal Structure
The interior is divided by welded partition plates, allowing separate chambers for different liquids. To avoid confusion in withdrawing liquids, some vehicles have touch-panel controls that can be operated through computer systems. Since there is a risk of the liquid inside the tank swaying and causing the vehicle to overturn, wave-dissipating plates are installed inside the tank.
Types of Tank Lorries
Tank lorries come in various sizes, including large, medium, and small.
1. Large Tank Lorries
Due to restrictions on vehicle width, the tank of large tank lorries is designed to be slender. Generally, tank capacities range from 12,000 to 20,000 liters.
They are mainly used to transport petroleum products from refineries to gas stations.
2. Medium Tank Lorries
Medium tank lorries typically weigh between 3 to 4 tons, and their tank capacity ranges from 3,000 to 8,000 liters. A single compartment can hold up to 4,000 liters.
They are suitable for refueling heavy machinery, transporting diesel, kerosene, and heavy oil, as well as transporting feed and food from factories.
3. Small Tank Lorries
Typically weighing between 2 to 3 tons, small tank lorries have a tank capacity of 2,000 to 4,000 liters. Their smaller size allows them to navigate narrow residential roads easily, and they can transfer diesel or kerosene to households.








